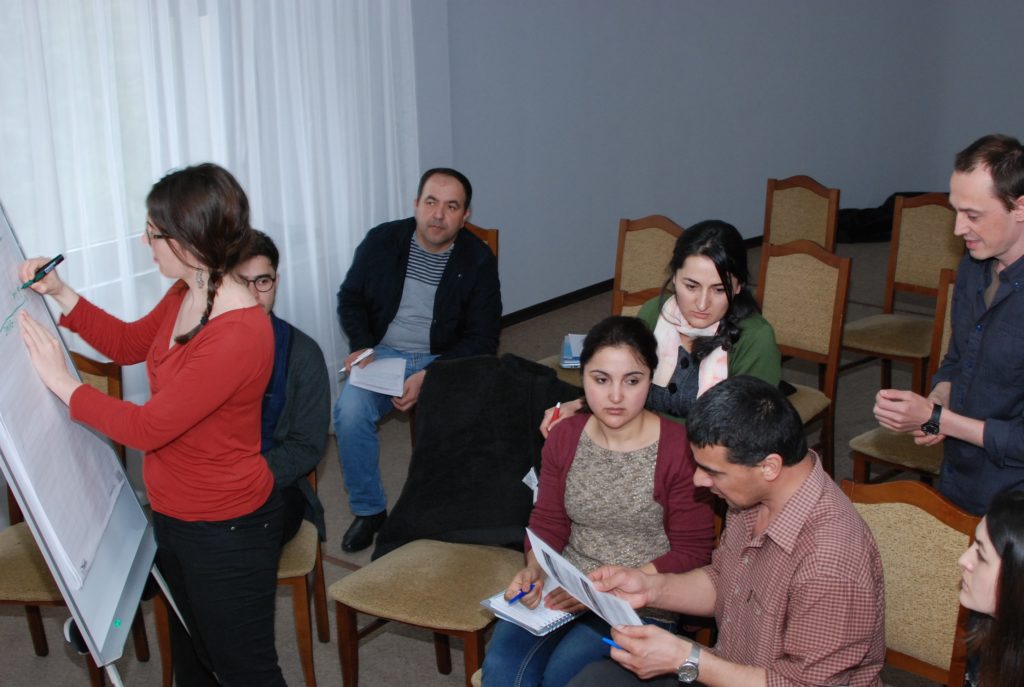
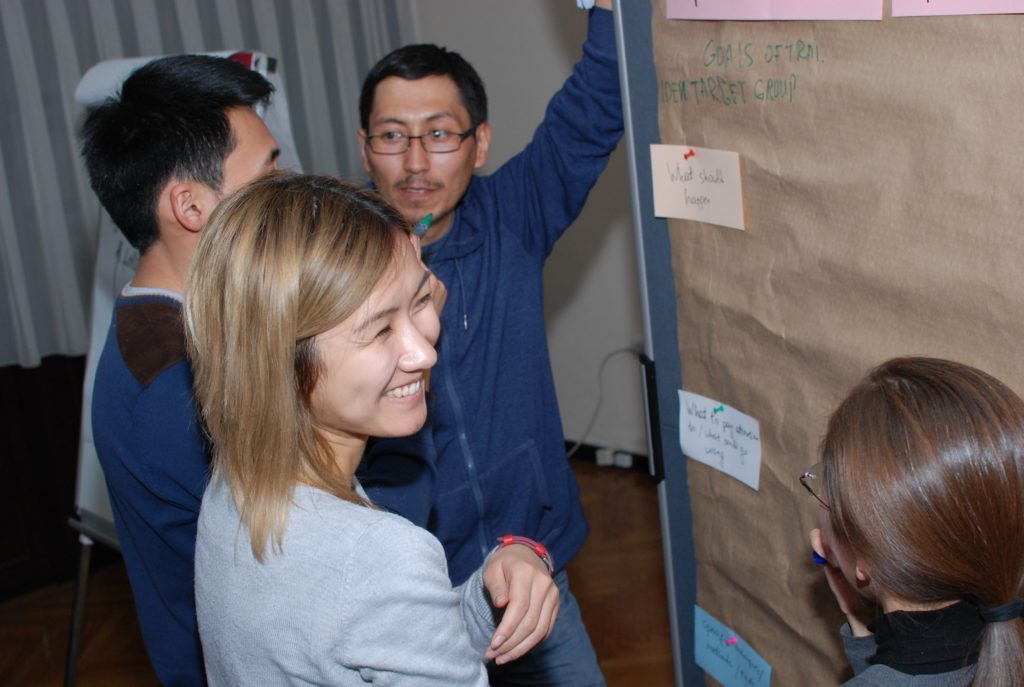
Dialogue (Central Asia)
In Central Asian countries, natural resource management is strongly centralized, which requires creating additional opportunities for involving the private sector and local people in the dialogue on the sustainable use of these resources taking into account economic, social and environmental aspects.
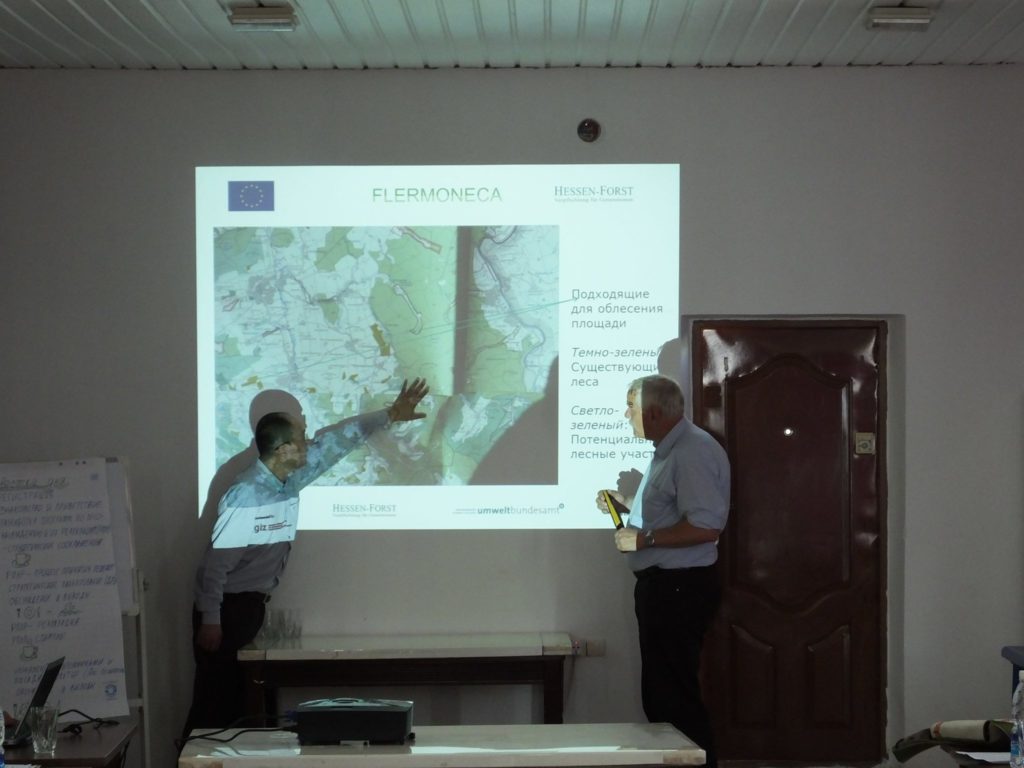
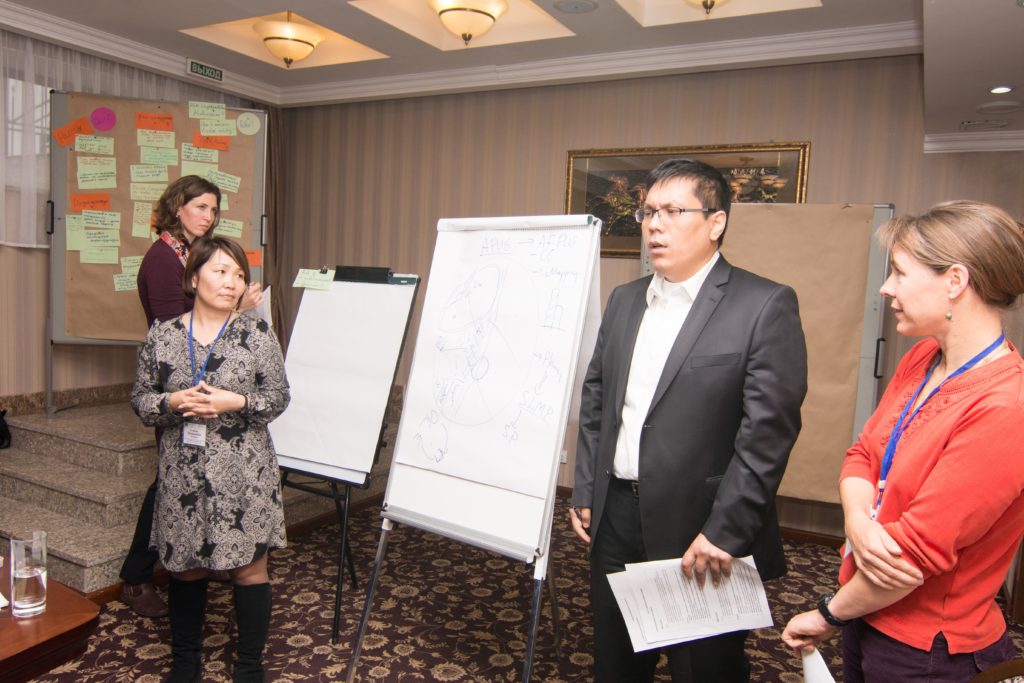
At the regional level, starting from 2017, Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH has been providing expert support in the development of the Regional Environmental Program for Sustainable Development in Central Asia (REPSD CA), important for all five countries. Together with other international partners, such as the United Nations Environment Program, GIZ supported technical meetings, meetings of national working groups and the regional working group (1st: December 2018 in Almaty; 2nd April 2019 in Tashkent; 3rd April 2019 in Almaty).
The meetings helped to reveal the national priorities of each of the countries participating in the Interstate Commission on Sustainable Development (ICSD). Only those topics that were of interest to two or more countries were submitted for discussion by the regional working group in order to ensure the regional nature of meetings. Numerous remote and personal discussions made it was possible to reach a consensus of the parties and to prepare draft REPSD CA, which was adopted in October 2019.
The regional cooperation of the GIZ Program with the ICSD Scientific Information Center was established in January 2016. The Program team assisted in the development of a systematic organizational process to strengthen the overall management and role of the ICSD among the founding countries; the capacity of ICSD bodies; the information policy and the workflowsystem, mechanisms and tools of external and internal communication; providing technical assistance to SIC branches according to their needs.
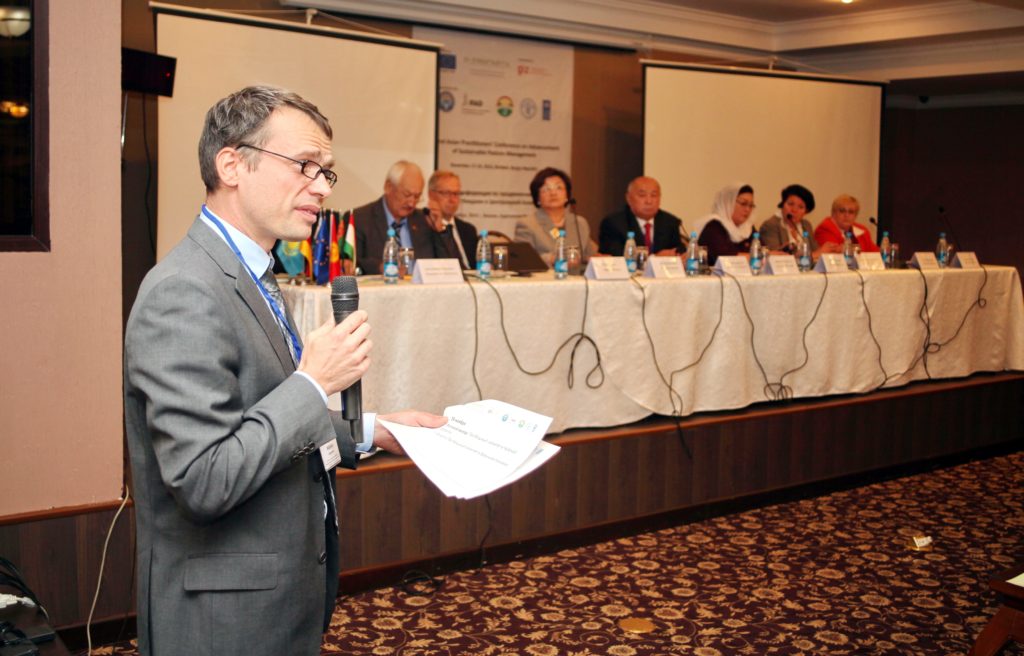
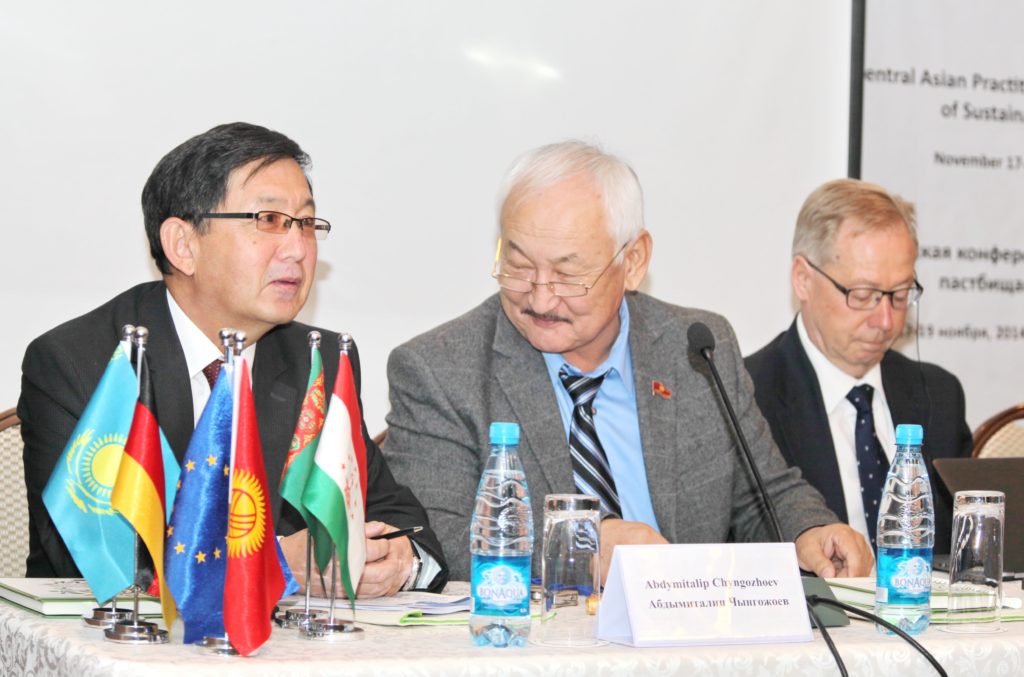
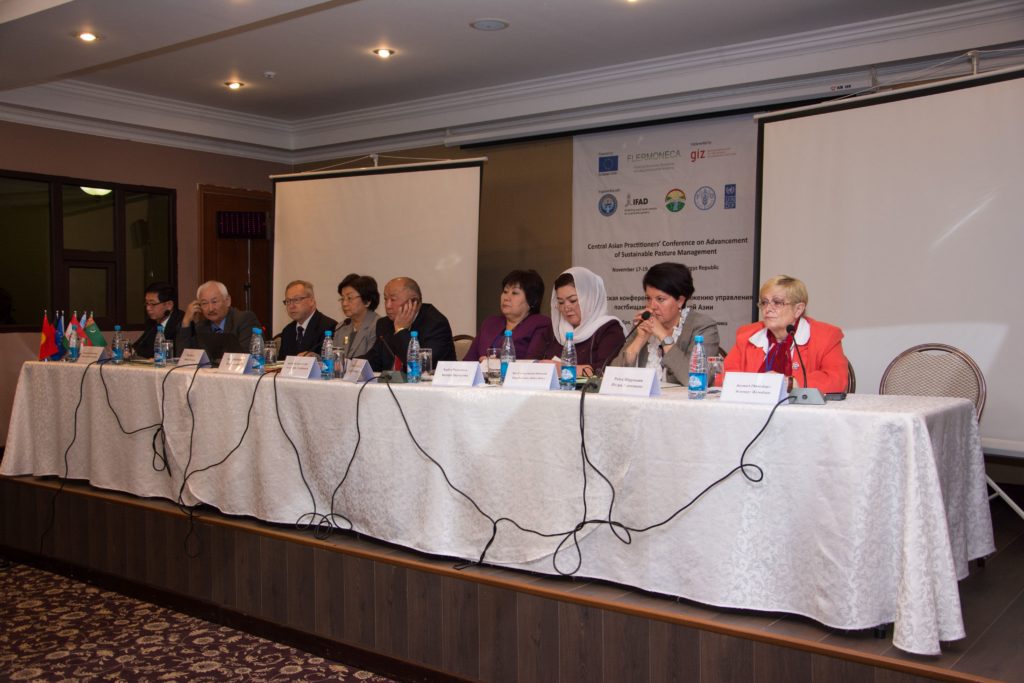
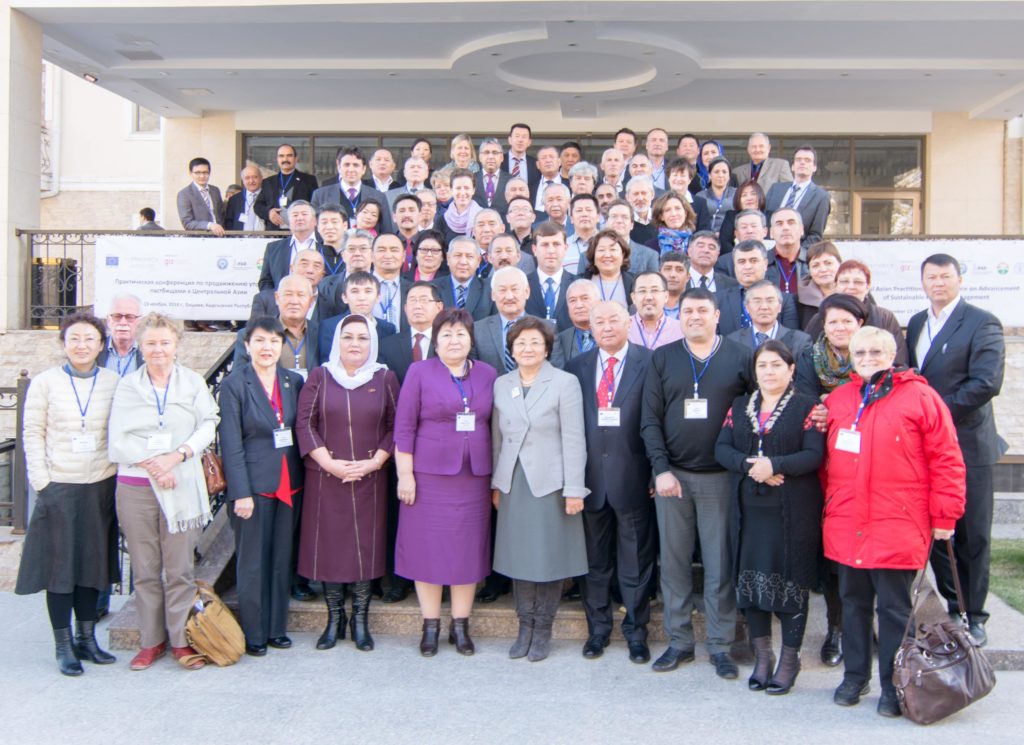
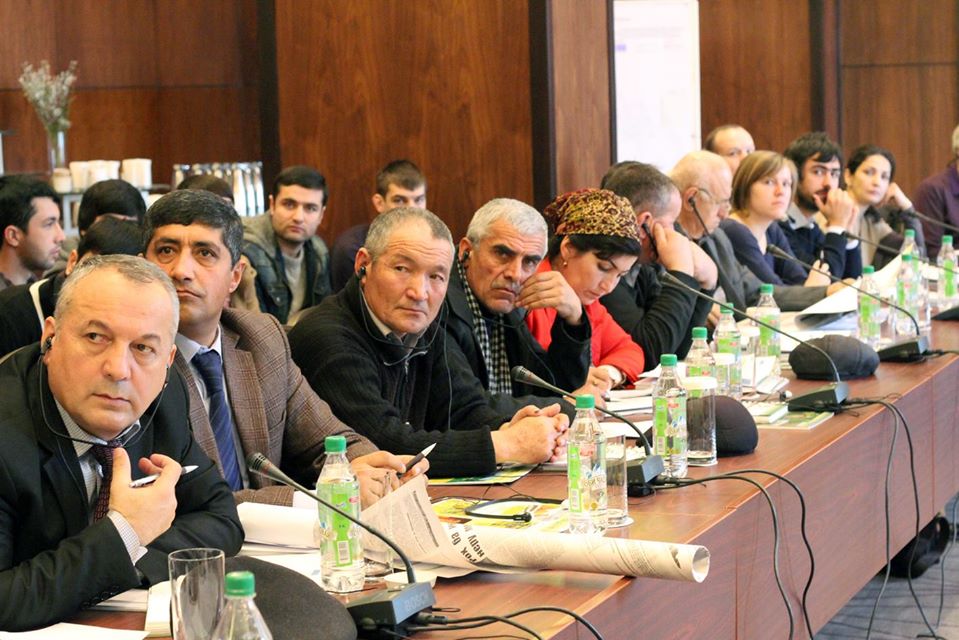
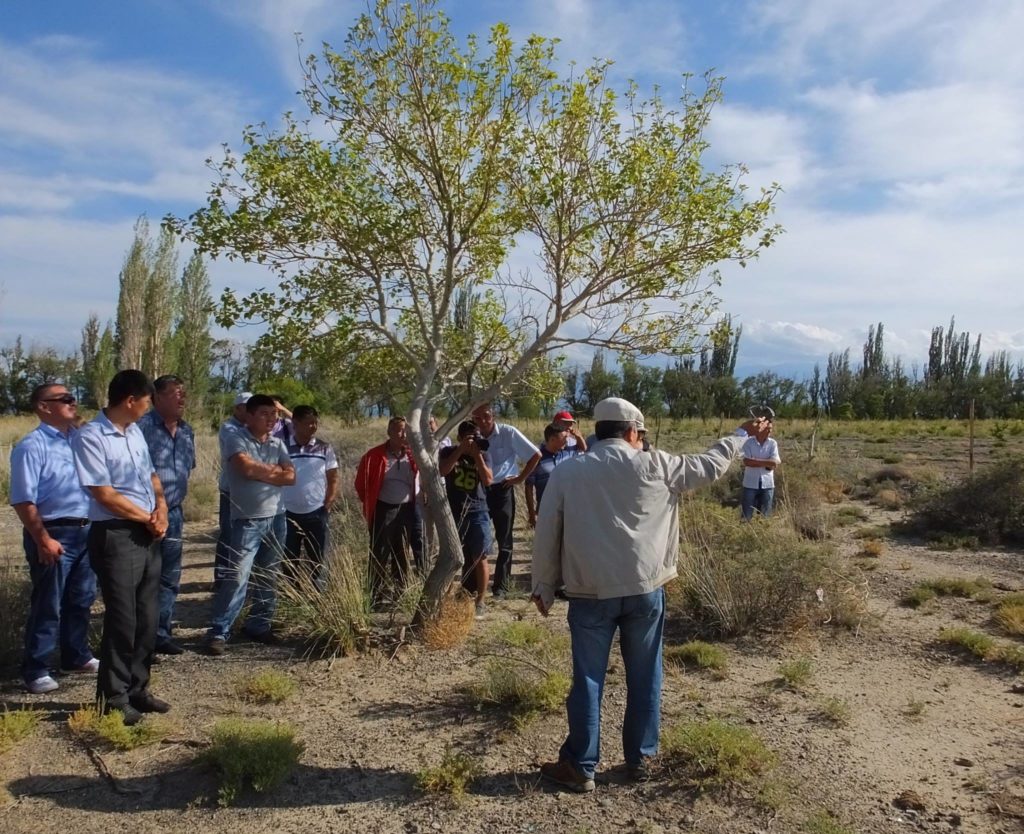
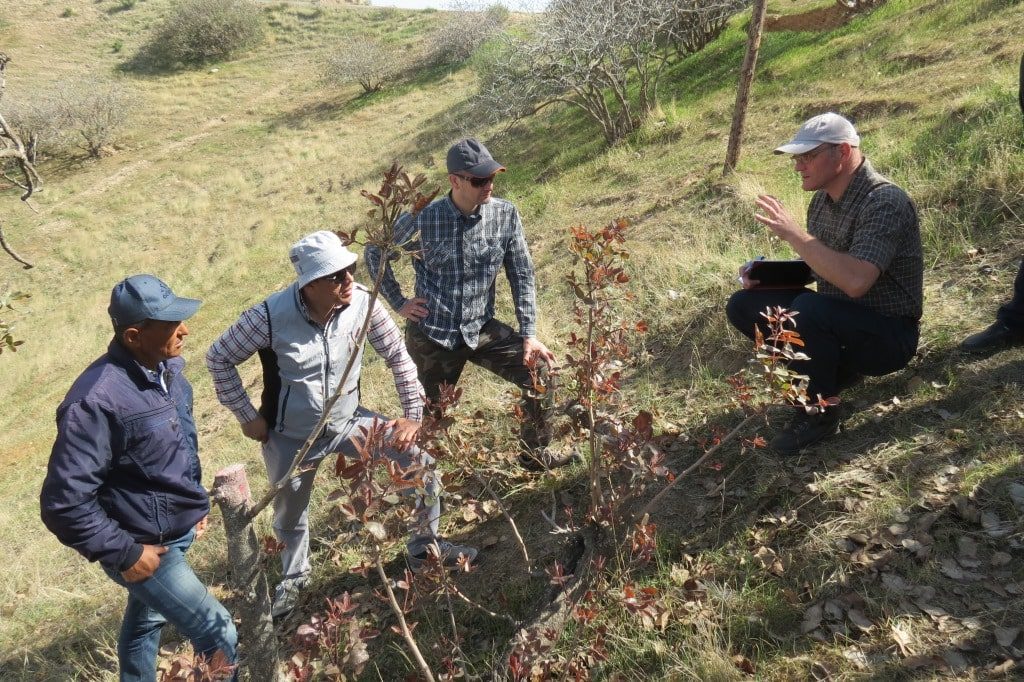
In 2014, Bishkek hosted the Practitioners’ Conference on Advancement of Sustainable Pasture Management in Central Asia. The purpose of this event for politicians and practitioners from Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan and international experts was to exchange experience and knowledge and join efforts to promote reforms in the pasture sector. Representatives of Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan had the opportunity to learn about international experience and the experience of their Kyrgyz and Tajik colleagues.
Conference participants were provided with innovative tools and approaches to managing
grazing lands, as well as proven mechanisms and processes. The program of the event included a field visit to one of the pasture committees in Chui oblast.
Some of the Important outcomes of the conference were the exchange of experience and knowledge, discussion of further actions and documentation of best practices and approaches. In addition to that, the results of the conference, an overview of the situation in the countries of the Central Asian region, analysis, comments and recommendations were included in the brochure “Sustainable Pasture Management in Central Asia”.
Field visits in Central Asia and study tours abroad help the exchange of experience and continuous training of practitioners and decision makers. Specifically, over the course of several years, long-term and short-term exchange visits were organized between representatives of the forestry services of Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan.
Besides, the Program conducted regional events such as:
- International round table “Sustainable Use and Conservation of Wild Animals in Tajikistan” (Dushanbe, Tajikistan, 2-3 November 2016)
- International Conference on Natural Capital for the Transition to a Green Economy (Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan, 30 June – 1 July 2016)
- International Conference on Sustainable Wildlife Management in Central Asia: Practical Experience and Next Steps (September 1-3, 2015 Ashgabat, Turkmenistan)
- International Conference “Ecosystem-Based Approach to Adaptation to Climate Change in Central Asia” (Dushanbe, Tajikistan, 9 April 2015)
These events help specialists to learn about the features and advantages of various natural resource management systems and establish long-term cooperation.
Dialogue (Kazakhstan)
In Central Asian countries, natural resource management is strongly centralized, which requires creating additional opportunities for involving the private sector and local people in the dialogue on the sustainable use of these resources taking into account economic, social and environmental aspects.
At the regional level, starting from 2017, Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (German Federal Enterprise for International Cooperation) has been providing expert support in the development of the Regional Environmental Program for Sustainable Development in Central Asia (REPSD CA), important for all five countries. Together with other international partners, such as the United Nations Environment Program, GIZ supported technical meetings, meetings of national working groups and the regional working group (1st: December 2018 in Almaty; 2nd April 2019 in Tashkent; 3rd April 2019 in Almaty).
The meetings helped to reveal the national priorities of each of the countries participating in the Interstate Commission on Sustainable Development (ICSD). Only those topics that were of interest to two or more countries were submitted for discussion by the regional working group in order to ensure the regional nature of meetings. Numerous remote and personal discussions made it was possible to reach a consensus of the parties and to prepare draft REPSD CA, which was adopted in October 2019.
The regional cooperation of the GIZ Program with the ICSD Scientific Information Center was established in January 2016. The Program team assisted in the development of a systematic organizational process to strengthen the overall management and role of the ICSD among the founding countries; the capacity of ICSD bodies; the information policy and the workflow system, mechanisms and tools of external and internal communication; providing technical assistance to SIC branches according to their needs.
At the national level, the GIZ Regional Program team provides support to national organizations in the implementation of private afforestation approaches. In accordance with the Forest Code [1, 6], private forestry is formed by artificial plantations of various purposes, nurseries and plantations created at the expense of individuals and non-state legal entities. The private afforestation approach aims to reduce the burden on natural forests and meet the growing demand for wood for industrial and energy purposes.
Due to close cooperation at different levels, the Program participates in joint development of guidelines for state support mechanisms for increasing the forest area through the use of private funds for afforestation. Work is also underway on implementation of these principles in the political dialogue on large-scale private investment in the forest sector.

At the local level, the Program supports the piloting of private afforestation in selected sites in Almaty, Akmola and Zhambyl regions. Regular consultations, support in collecting technical information and conducting activities to improve skills and enhance the capacity of stakeholders accompany all processes. Kazakhstan is one of the countries that may be most affected by climate change. Extreme weather events, such as heat waves and torrential rains followed by floods are expected to become more intense and frequent. Melting glaciers in the highlands of Central Asia will reduce the amount of water available for irrigation in late summer and will lead to an increase in water flow in spring. All this will adversely affect the economy, agriculture and aggravate environmental and social problems. Recognizing the need for action to reduce negative changes, Kazakhstan ratified the Paris Agreement in 2016, thereby pledging to help keep global average temperature growth below 2°C compared with the pre-industrial era. This means that the country must reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 15 percent, and in the case of international support – by 25 percent by 2030 from the 1990 level. The implementation of the 2013 Concept for Transition to a Green Economy should primarily help in fulfilling these obligations.
The Paris Agreement also clearly expresses the need for each country to participate in adaptation planning processes and implementation of mitigation measures. GIZ and the NAP Global Network are currently supporting line ministries in identifying opportunities for developing adaptation measures and their practical implementation at the national and regional levels. In this vein, the GIZ Regional Program closely cooperates with the regional project “Ecosystem-Based Adaptation to Climate Change in High Mountainous Regions of Central Asia”.
Dialogue (Kyrgyzstan)
In Central Asian countries, natural resource management is strongly centralized, which requires creating additional opportunities for involving the private sector and local people in the dialogue on the sustainable use of these resources taking into account economic, social and environmental aspects.
At the regional level, starting from 2017, Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (German Federal Enterprise for International Cooperation)has been providing expert support in the development of the Regional Environmental Program for Sustainable Development in Central Asia (REPSD CA), important for all five countries. Together with other international partners, such as the United Nations Environment Program, GIZ supported technical meetings, meetings of national working groups and the regional working group (1st: December 2018 in Almaty; 2nd April 2019 in Tashkent; 3rd April 2019 in Almaty).
The meetings helped to reveal the national priorities of each of the countries participating in the Interstate Commission on Sustainable Development (ICSD). Only those topics that were of interest to two or more countries were submitted for discussion by the regional working group in order to ensure the regional nature of meetings. Numerous remote and personal discussions made it was possible to reach a consensus of the parties and to prepare draft REPSD CA, which was adopted in October 2019.
The regional cooperation of the GIZ Program with the ICSD Scientific Information Center was established in January 2016. The Program team assisted in the development of a systematic organizational process to strengthen the overall management and role of the ICSD among the founding countries; the capacity of ICSD bodies; the information policy and the workflow system, mechanisms and tools of external and internal communication; providing technical assistance to SIC branches according to their needs.
To support the dialogue at the national and local levels, the Program provided support to SAEPF in forestry sector reform piloting. The reform is based on the principles of decentralization and partnership between the public, private sectors and local communities. The piloting process is coordinated by the Consultative Coordinating Council (CCC), which consists of representatives of various government agencies, development partner organizations and civil society. Piloting process, the results achieved, problems and solutions are discussed at CCC meetings. CCC fosters dialogue among stakeholders.
We also contributed to raising awareness of key partners, such as the SAEPF, the Ministry of Economy, the Ministry of Agriculture, Food Industry and Land Reclamation, the Hydrometeorology Agency under the Ministry of Emergencies of the Kyrgyz Republic (Kyrgyzhydromet), the National Statistics Committee, the Department of Water Resources, KyrgyzGiprozem, I. Razzakov Kyrgyz State Technical University on measurement, reporting and verification (MRV) and climate reporting in international conventions.
This resulted in a Memorandum of Understanding being signed by 12 government institutions in order to comply with national spatial data standards.
The SAEPF Consultative Coordinating Council (CCC) is called upon to direct and coordinate efforts to pilot the reform. It consists of representatives of various government agencies, development partner organizations and civil society. During the piloting period, the Council held 19 meetings to discuss the piloting process, the results, problems, and solutions. CCC helps strengthen dialogue between stakeholders from various sectors of the economy in order to discuss issues related to sustainable forest management.
Dialogue (Tajikistan)
In Central Asian countries, natural resource management is strongly centralized, which requires creating additional opportunities for involving the private sector and local people in the dialogue on the sustainable use of these resources taking into account economic, social and environmental aspects.
Starting from 2017, Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (German Federal Enterprise for International Cooperation) has been providing expert support in the development of the Regional Environmental Program for Sustainable Development in Central Asia (REPSD CA), Besides expert support, the Program supported technical meetings, meetings of national working groups and the regional working group (1st: December 2018 in Almaty; 2nd April 2019 in Tashkent; 3rd April 2019 in Almaty). GIZ with other international partners (United Nations Environment Program, CAREC) is actively involved in this process.
The meetings helped to reveal the national priorities of each of the countries participating in the Interstate Commission on Sustainable Development (ICSD). Only those topics that were of interest to two or more countries were submitted for discussion by the regional working group in order to ensure the regional nature of meetings. Numerous remote and personal discussions made it was possible to reach a consensus of the parties and to prepare draft REPSD CA, which was adopted in October 2019.
The regional cooperation of the GIZ Program with the ICSD Scientific Information Center was established in January 2016. The Program team assisted in the development of a systematic organizational process to strengthen the overall management and role of the ICSD among the founding countries; the capacity of ICSD bodies; the information policy and the workflow system, mechanisms and tools of external and internal communication; providing technical assistance to SIC branches according to their needs.
At the national level, the GIZ Program promotes dialogue among various stakeholders and improves the legal framework. Specifically, the Program carried out a pasture management institutional analysis, which reflects the institutional and legal structure and distribution of roles and responsibilities in the pasture management system of Tajikistan. The document also suggests potential entry points for future donor-funded activities that could strengthen the institutional framework for sustainable pasture management in Tajikistan.
The GIZ Program assisted in the development of the Law on Pasture and related regulations. The new law was developed in 2018 and approved by the government in 2019. Besides a number of regulations were developed such as the Regulation on the Machlis Commission on Pasture Regulation and Use , the Regulation on Definition of an Authorized Body for State Administration and Use of Pastures and the Charter for pasture users.
In Tajikistan, GIZ also helped create and establish a Regional Pasture Network. This informal platform for communication brings together more than 50 governmental, international and non-governmental organizations, as well as scientists and researchers. It works to support supporting national dialogue and knowledge sharing based on local practical experience of platform members. The draft Charter of the Pasture User Unions developed by members of the Platform makes it easier for users to create pasture unions and self-organize.
Dialogue (Turkmenistan)
In Central Asian countries, natural resource management is strongly centralized, which requires creating additional opportunities for involving the private sector and local people in the dialogue on the sustainable use of these resources taking into account economic, social and environmental aspects.
At the regional level, starting from 2017, Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (German Federal Enterprise for International Cooperation) has been providing expert support in the development of the Regional Environmental Program for Sustainable Development in Central Asia (REPSD CA), important for all five countries. Together with other international partners, such as the United Nations Environment Program, GIZ supported technical meetings, meetings of national working groups and the regional working group (1st: December 2018 in Almaty; 2nd April 2019 in Tashkent; 3rd April 2019 in Almaty).
The meetings helped to reveal the national priorities of each of the countries participating in the Interstate Commission on Sustainable Development (ICSD). Only those topics that were of interest to two or more countries were submitted for discussion by the regional working group in order to ensure the regional nature of meetings. Numerous remote and personal discussions made it was possible to reach a consensus of the parties and to prepare draft REPSD CA, which was adopted in October 2019.
Региональное сотрудничество программы GIZ с Научно-информационным центром МКУР было положено в январе 2016 г. Команда программы оказывала содействие в The regional cooperation of the GIZ Program with the ICSD Scientific Information Center was established in January 2016. The Program team assisted in the development of a systematiс organizational process to strengthen the overall management and role of the ICSD among the founding countries; the capacity of ICSD bodies; the information policy and the workflow system, mechanisms and tools of external and internal communication; providing technical assistance to SIC branches according to their needs..
In 2016-2017, at the request of the Regional Program, SIC ICSD prepared a situational analysis of climate change in Turkmenistan.
When designing projects and regulations to the Law on Pastures, the Program team together with the international expert Dr. Sarah Robinson and local experts held regular meetings with members of the working group on improving pasture legislation in Ashgabat (the most recent meeting was held in March 2019). There were also field meetings and consultations with all stakeholder: local authorities, private cattle herders, the local community in the Dyanev district of the Lebap region and the Baharly district of the Akhal region (the most recent meeting was held in June 2018).
Dialogue (Uzbekistan)
In Central Asian countries, natural resource management is strongly centralized, which requires creating additional opportunities for involving the private sector and local people in the dialogue on the sustainable use of these resources taking into account economic, social and environmental aspects.
At the regional level, starting from 2017, Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (German Federal Enterprise for International Cooperation) has been providing expert support in the development of the Regional Environmental Program for Sustainable Development in Central Asia (REPSD CA), important for all five countries. Together with other international partners, such as the United Nations Environment Program, GIZ supported technical meetings, meetings of national working groups and the regional working group (1st: December 2018 in Almaty; 2nd April 2019 in Tashkent; 3rd April 2019 in Almaty).
The meetings helped to reveal the national priorities of each of the countries participating in the Interstate Commission on Sustainable Development (ICSD). Only those topics that were of interest to two or more countries were submitted for discussion by the regional working group in order to ensure the regional nature of meetings. Numerous remote and personal discussions made it was possible to reach a consensus of the parties and to prepare draft REPSD CA, which was adopted in October 2019.
The regional cooperation of the GIZ Program with the ICSD Scientific Information Center was established in January 2016. The Program team assisted in the development of a systematic organizational process to strengthen the overall management and role of the ICSD among the founding countries; the capacity of ICSD bodies; the information policy and the workflow system, mechanisms and tools of external and internal communication; providing technical assistance to SIC branches according to their needs.
Piloting (Kazakhstan)
The Kazakhstan’s developing economy stimulates the demand for wood products, while low forest cover (4.5%) encourages a careful attitude to forest resources. This explains why wood products are currently imported from abroad. At the same time, there are numerous possibilities to increase forest areas and improve the quality of wood.
One of them is private sector involvement. In accordance with the Forest Code [1, 6], individuals and non-government legal entities are entitled to establish and grow plantations for various purposes, create nurseries and forest stands.
In 2015, with the technical support of Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (German Federal Enterprise for International Cooperation), a feasibility study was carried out on measures for private afforestation. This resulted in a joint decision by GIZ and the Committee on Forestry and Wildlife (CFW) of the Ministry of Ecology, Geology and Natural Resources on a pilot project as the basis for developing an effective mechanism of state co-financing of private afforestation.
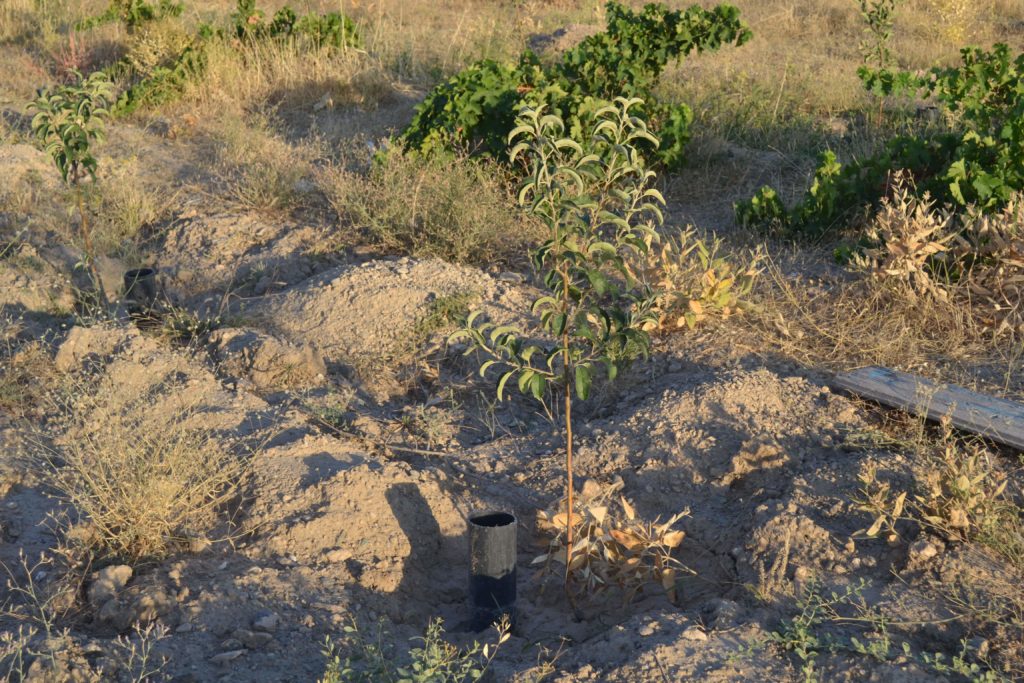
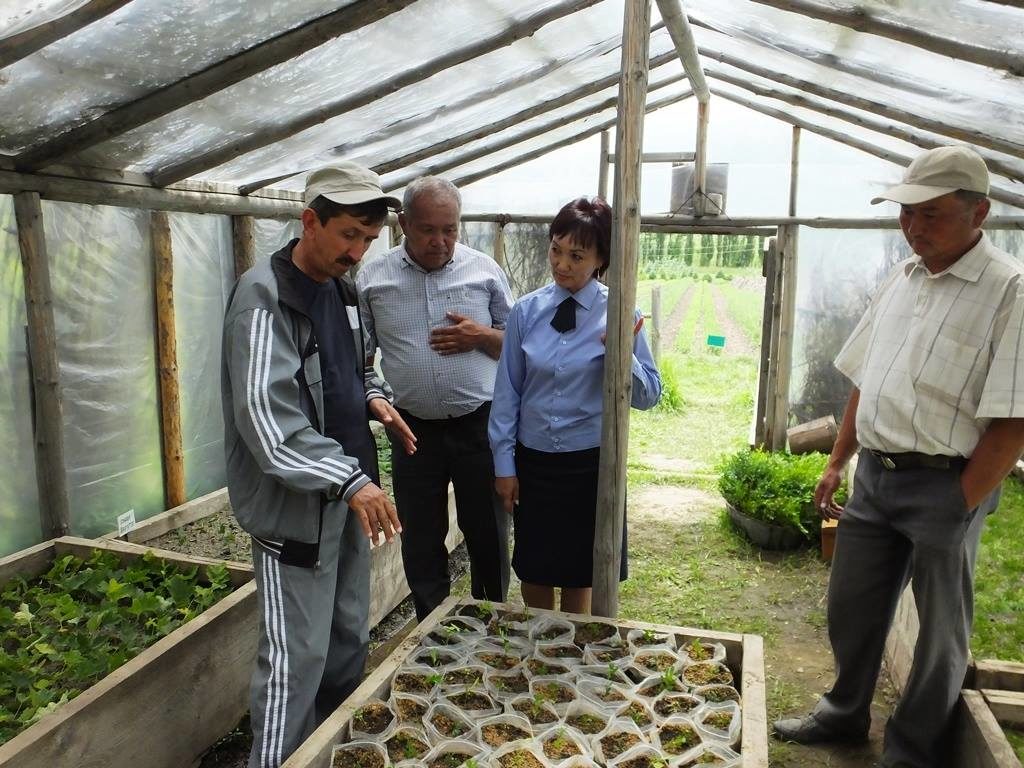
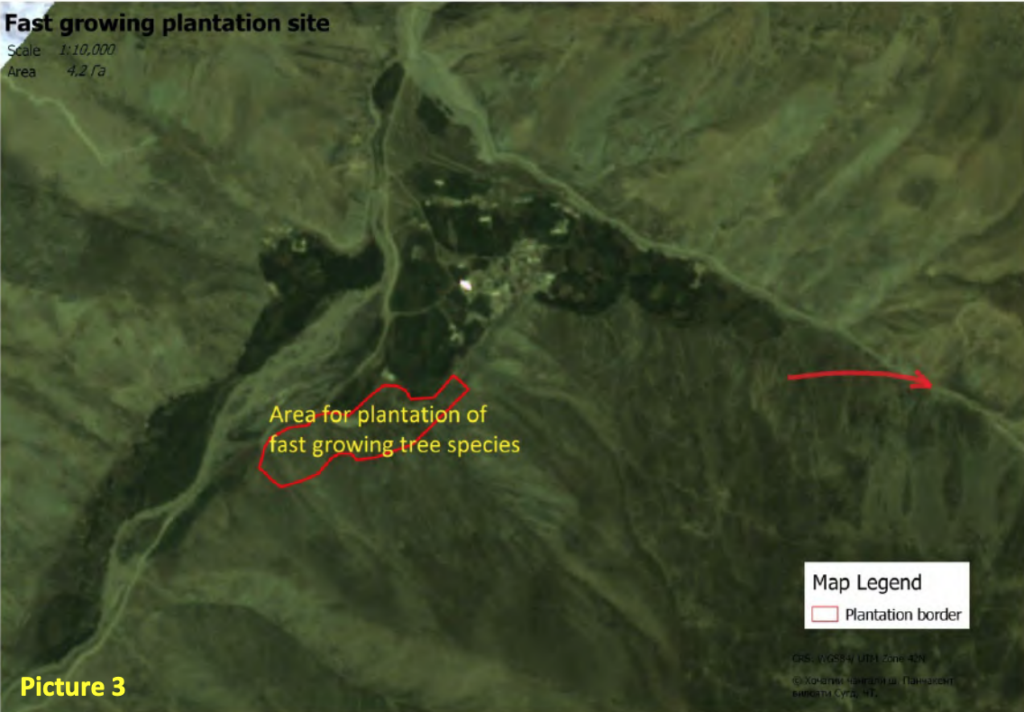
In 2016, fast-growing tree species were planted in (6) six small experimental sites in three regions of the country – Almaty, Akmola and Zhambyl. Along with monitoring and data collection, GIZ experts supported the development of a regulatory framework governing private investment in afforestation.
Based on relevant international experience and consultations with national stakeholders (top-down approach), the GIZ Regional Program supports the development of a common strategy and recommendations on the concept of private afforestation, including an effective state support program. Pilot activities in different regions of the country ensure the accumulation of practical experience and data (bottom-up approach).
The pilot phase revealed that the establishment of plantations of fast-growing tree species, such as poplar is feasible in different regions of Kazakhstan. The country has the necessary conditions in place for the successful implementation of such initiatives – the availability of land, suppliers capable of providing quality services with the necessary experience and expert knowledge, landowners who demonstrate interest in such initiatives and forest nurseries as suppliers of planting material.
Testing of the Regulation on functional zoning in the Kyrgyz Republic
In December 2022, the Forest Service under the Ministry of Agriculture of the Kyrgyz Republic began testing the Regulation on functional zoning of the state forest fund of the Kyrgyz Republic (hereinafter – the Regulation) in forest enterprises in Arky, Talas and Issyk-Kul.The Regulation is being tested with the support of the regional programme “Integrative and Climate-sensitive Land Use in Central Asia”, implemented by Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (German Society for International Cooperation) on behalf of the German government. It is expected that the testing of functional zoning will allow to practice the interaction of the working group members on the implementation of the tasks, interaction of the Forestries with the local communities and other stakeholders, implementation of the procedures described in the Regulation; and it will allow to identify potential shortcomings and gaps of the Regulation.
Piloting (Kyrgyzstan)
In Kyrgyzstan, forests are located in mountain ranges at altitudes from 700 to 3600 m above sea level, occupying only 5.61% of the country’s total area. According to the Forest Code, all forest resources are valuable and protected by the state. However, existing forests are reduced due to negative economic conditions and demographic growth.
To preserve and restore forest areas, since 2015, the State Agency on Environment Protection and Forestry of the Kyrgyz Republic (SAEPF), with the support of the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (German Federal Enterprise for International Cooperation) Regional Program, has been piloting the forest sector reform.
The piloting is aimed at testing and adapting innovative methods in forestry management, in six, and subsequently (2017) in 20 pilot forestry enterprises. These new methods provide for the involvement of the local population and LSG bodies in management and decision-making.
It is expected that the reform will result in an increase in forest cover, the development of forest environmental functions and economic benefits for both the local population and the state.
The main tasks of piloting:
- Analyze and assess the current situation in the forest sector of the Kyrgyz Republic;
- Develop proposals for improving forestry and related legislation;
- Test and implement new approaches in forestry financial management by enabling experimental forestry enterprises to distribute and use funds to finance sustainable forest management and personnel;
- Study possibilities of introducing modern methods in forestry management by separating the economic, control and regulatory functions;
- Explore possibilities of introducing new approaches to pilot forestry enterprise management, including those based on the principles of public-private partnership in accordance with the legislation of the Kyrgyz Republic;
- Introduce the principles of a green economy in pilot forestry enterprises;
- Determination of the main directions, methods and terms of the forest reform.
Piloting approaches:
- in agreement with the authorized state body for environmental protection, forestry and hunting, using budget funds (including special ones) in accordance with the objectives of the reform; this also applies to funds released during the reform process in the manner established by the legislation of the Kyrgyz Republics;
- optimizing the forestry internal structure to adapt to sustainable forest management in the region, including a review of the staffing table, functional responsibilities and the personnel management process;
- effectively managing state property of the pilot forest enterprises to achieve sustainable forest management in the manner prescribed by the legislation of the Kyrgyz Republic;
- determining the amount of monetary allowance to employees of pilot forestry enterprises based on the labor participation rate (LPR) and personal labor contribution of employees in accordance with the legislation Kyrgyz Republic;
- channeling resources, including monetary ones, to areas that most successfully ensure the effectiveness of pilot forest enterprises in the manner prescribed by the legislation of the Kyrgyz Republic;
- using income to cover the costs of providing services and maintaining forestry facilities, silvicultural and forestry activities according to the legislation of the Kyrgyz Republic;
- transferring certain silvicultural and forestry operations to entities, including on the basis of public-private partnership in accordance with the legislation of the Kyrgyz Republic;
- organizing and providing tourist and recreational services according to the legislation of the Kyrgyz Republic;
- in agreement with the authorized state body for environmental protection, forestry and hunting, approving plans for the financial and economic activities of entities operating in pilot forestry enterprises.
Four rounds of data collection in six (6) pilot forestry enterprises were conducted as part of the forest sector reform piloting in the Kyrgyz Republic in order to monitor the piloting process, document the experience gained for subsequent analysis and recommendations.
In December 2017, based on the request of the SAEPF to the Government of the Kyrgyz Republic, the piloting was extended until 2021.
Piloting (Tajikistan)
Forests play a crucial role in the life of the rural population of Tajikistan. Being an important source of income, firewood, fodder plants, herbs, fruits and nuts are sold locally. Forests also fulfill a major function of regulating water balance and protecting the population against natural disasters. Therefore, restoration and protection of forests are crucial when it comes to increasing resilience and enhancing adaptation to climate change. Unfortunately, after the collapse of the Soviet Union, an increased demand for firewood led to widespread deforestation. This has made the country vulnerable to climate change. Conflicts over land-use rights between leskhozes and the local population also result in the overexploitation and degradation of forest resources.
Successful forest management in Tajikistan requires a multi-level and multi-faceted approach. In this vein, Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (German Federal Enterprise for International Cooperation) Program has supported the pilot implementation of integrated forest management approaches through restoration and conservation. It is just as important as supporting relevant forest management bodies in charge of planning, managing and monitoring sustainable forest management.
The Joint Forest Management (JFM) approach allows local people to participate in the management and restoration of degraded forests with obvious benefits for both the local population and forestry enterprises. Local forest users sign land lease agreement with state forestry enterprises (leskhozes) for 20 years with an option to extend. This enables them to use forest products in exchange for afforestation of degraded areas. Besides, the local population and leskhozes are involved in forest planning and management and the respective monitoring activities.
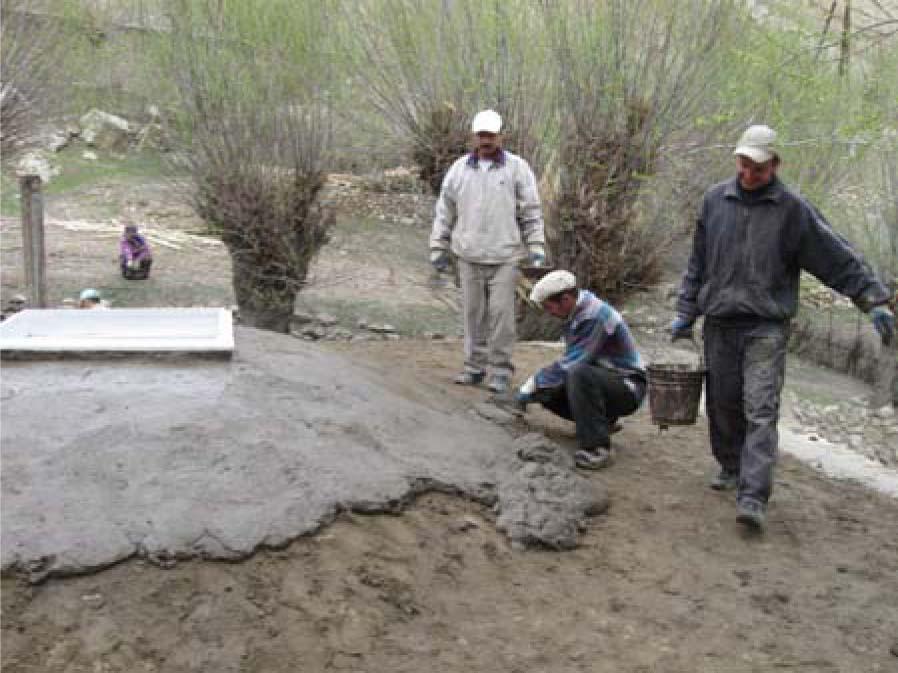
The Program team also supports planting fast-growing tree species on common lands near settlements. Such species can be used for logging, thus preventing deforestation of nearby areas. One of the demonstration plots is located near the settlement of Gazza equipped with pipelines for seedling irrigation.
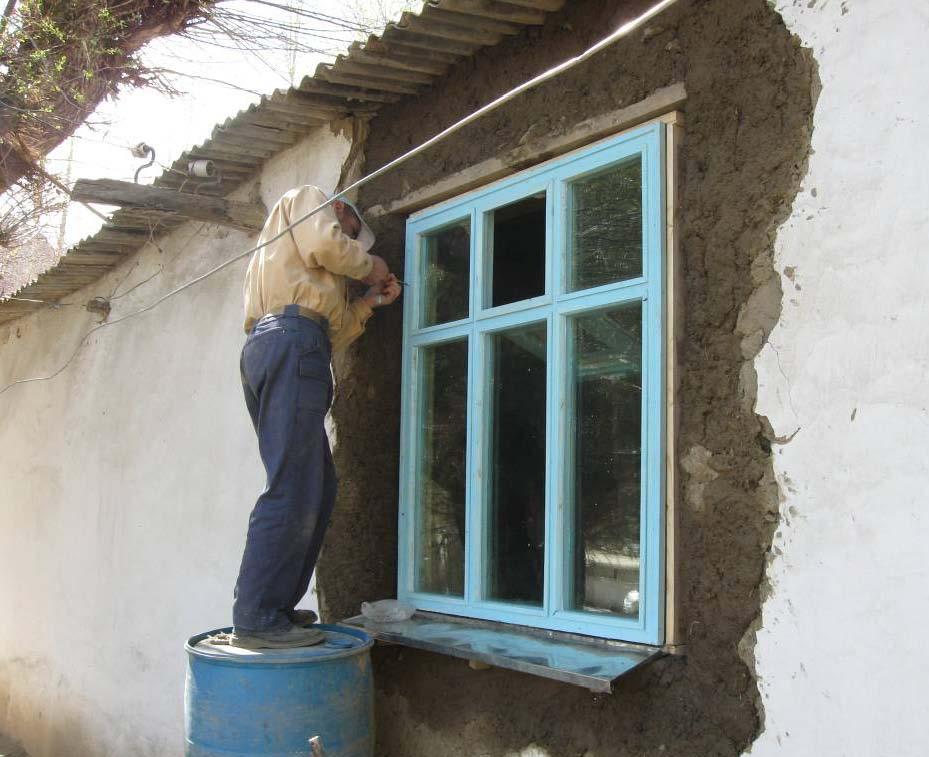
In addition to that, to reduce the felling of trees for heating purposes, local residents were trained in energy-saving technologies in window and door insulation and house construction.
Another effective approach to reforestation of degraded areas was the introduction of a financial incentives for the population.
The centerpiece of the approach design is the establishment of deposit accounts for forest users, which are replenished with funds intended for the purchase of the necessary planting or other materials. This is called the Saving Book Approach (SBA). Forest users together with their local leskhoz develop an action plan that stipulates the amount that will be available to them if they meet the objectives of the previous year. As the income from the forest plot grows, annual revenues from SBA decrease. The SBA implementation term varies depending on the specific conditions of the forest area and species. SBA has made an invaluable contribution to reforestation in Tajikistan.

Besides efforts at the national level (legal framework, policies, monitoring systems, new
approaches, etc.), GIZ also provides technical support at the institutional level to improve forest management, implement integrated land management, strengthen the capacity of using digital technology, etc.
The Program also supports private sector participation in the sustainable management of natural resources and the introduction of market-based approaches. For this, various technologies have been developed to increase the efficiency of the use of natural resources, such as forests and water. These technologies are adapted to local conditions at the household and community level and standardized for further use.
Piloting (Turkmenistan)
Independence gained by the Central Asian countries – Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan – after the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 caused serious land management issues aggravated by the economic, social, and environmental crisis. The historical development of irrigation projects, proliferation of livestock on pastures and the re-profiling of agricultural land in the steppe during communism have made land degradation a critical issue in the region that threatens the current and future livelihoods of the rural population.
Turkmenistan plans to pilot the Law on Pastures and develop important regulatory documents. The country also works on improving the legal framework of the forest sector. Some new regulatory documents are now being coordinated with the Ministry of Agriculture and Environment Protection of Turkmenistan.
The most important features of the Law on Pastures include the following:
- The Law guarantees the right to pastures for all pasture users (state, private and collective). An overview of various pasture management systems in the context of property right shows that today’s priority is public pasture management, which is the key to effectiveness. Public management promotes animal mobility compared to long-term lease of pastures, which usually limits livestock movement within a given territory. In Turkmenistan, the state is also involved in livestock raising, which also contributes to livestock mobility. The Law does not encourage a specific pasture management system, but offers various systems for sustainable pasture management with the participation of private, individual and collective pasture users.
- The Law provides for equal and fair access to pastures for all users (state and private livestock owners), giving them equal rights and enabling them to create associations of pasture users. The main objective of the Law is to provide access to pastures and in many respects to facilitate the related procedure.
- The Law promotes the environmentally sustainable use of rangelands on the basis of high mobility (movement) of livestock, which reduces the load on pastures and prevents their degradation. For this, the Law contains provisions on pasture rotation, moving livestock outside the designated pasture lands, and even distribution of livestock across pastures. In addition to that, the environmentally sustainable use of pastures is supported by the provision on paid use of pastures and short-term lease agreement based on pasture management plans.
- The Law lays down important elements targeting adaptation to climate change. The specific articles of the Law are discussed below;
- Finally, the Law on Pastures was developed in full accordance with the Turkmenistan Land Code which provides the legal framework for the control, management and distribution of pasture lands, as well as the legal regime for pasture use, the rights and obligations of land (pasture) users, etc.
Piloting (Uzbekistan)
Uzbekistan is a poorly forested country. Yet, forest ecosystems play an important economical and environmental role. The forest ecosystems have a great effect on the climate, the availability of clean water, clean air, protects agricultural land, provides places for comfortable living and recreation, and preserves the diversity of wildlife. Currently, the state forest fund of Uzbekistan is 11 million hectares, the forested area is only 3.5 million hectares, of which 12 percent are mountain forests, 7 percent of the valley / plain forest and 81 percent are deserts.
One of main challenges is the effective management of forestry, including involving the local population in maintaining and increasing the area of local walnut and fruit tree such as pistachio, hazelnut and almond. In close cooperation with national and local partners, the Program seeks to involve local residents in joint forest management, restoration of forest ecosystems, conservation of biodiversity and improvement of the well-being of the local population through effective forest management.

The Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (German Federal Enterprise for International Cooperation) Program team, together with the State Forestry Committee of the Republic of Uzbekistan, helped design a joint forest management model. It includes creating sea buckthorn and wild rose plantations in the state forest fund. This will create an additional source of income for local resident and a source of raw materials for the pharmaceutical industry.
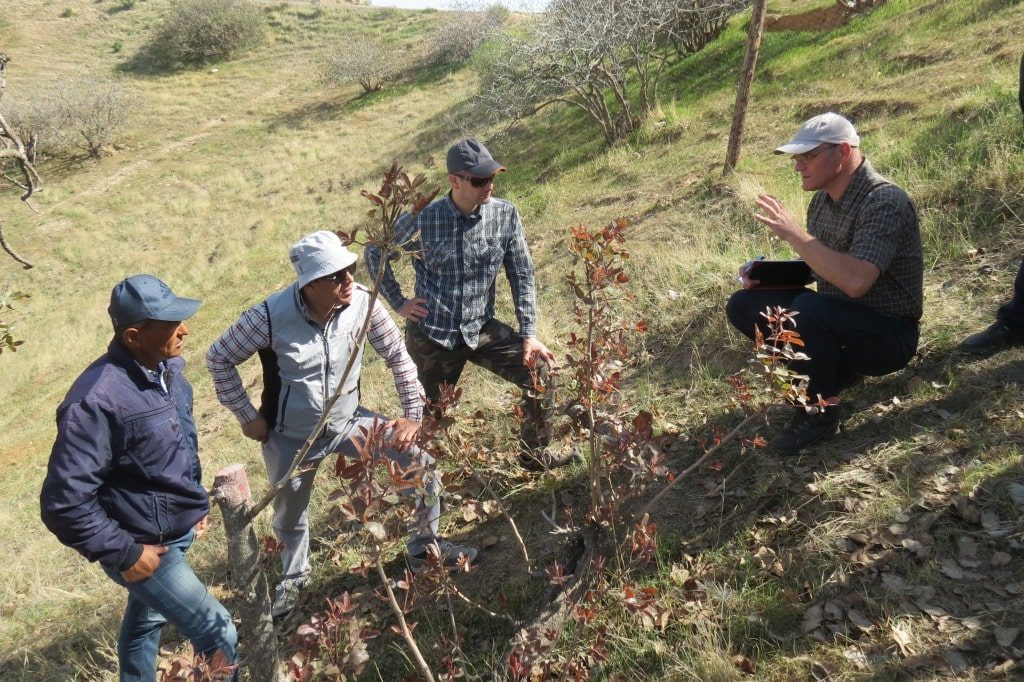
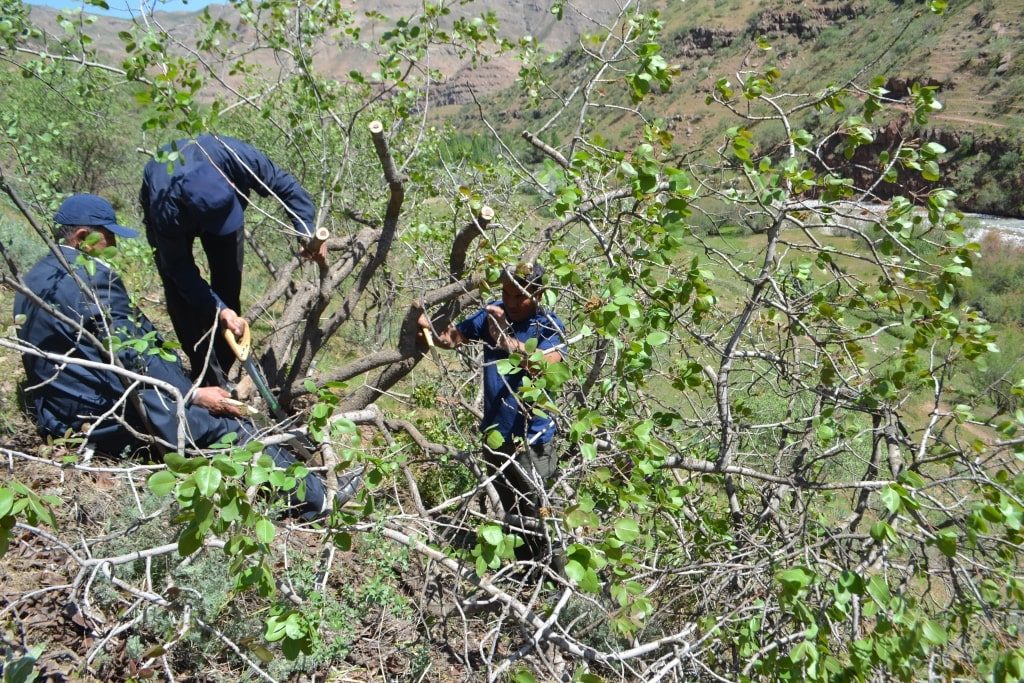
The Program provides support to the State Forestry Committee in introducing a new approach to joint forest management on five demonstration plots in Bobotog and Gissar forestry enterprises, Surkhardarya region. The plots mainly have a combination of natural species and pistachio trees aged 60-70 years. The proper care for these trees (pruning, sanitary cleaning, grafting) increases the productivity of trees leading to the appearance of varietal and economically valuable crops. Combined planting of pistachios and almonds, and some medical plants, such as Ferula and saffron, is also practiced.
The joint forest management approach helps to involve local residents in the management of natural resources and make them more responsible about their economic activities. At the same time, efforts are made to reduce land degradation due to overgrazing.
Earlier, since 2012, the program had worked on pasture management. Thus, residents of the Farish district, where the program piloted new approaches, were trained in effective pasture management planning. To reduce pasture overload, people were offered opportunities to use alternative sources to generate income.
Education (Kazakhstan)
Since 2009, Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (German Federal Enterprise for International Cooperation) Program has been supporting knowledge exchange on sustainable land management both between different sectors and at different levels, including local, national and regional.
The GIZ Regional Program in Kazakhstan, in cooperation with international organizations – UNDP and World Bank projects conducted training activities on development of private afforestation. In addition to that, during workshops and field trips at the national level, the Program presented and discussed the results of piloting, received recommendations from stakeholders and agreed on joint actions.
The Program plans to continue working on raising awareness and involving representatives of state, scientific, private organizations and NGOs in developing a system of state support for afforestation and engaging private forest users.
The Program also provides consultations and support in the development of effective coordination and organizational development mechanisms for the Interstate Commission on Sustainable Development (ICSD) in Central Asia, including strengthening the capacity of the ICSD Science and Information Center in Kazakhstan. K-Link and K-DMS knowledge management mechanisms are being introduced as document and information management tools for ICSD bodies and structural units.
Education (Kyrgyzstan)
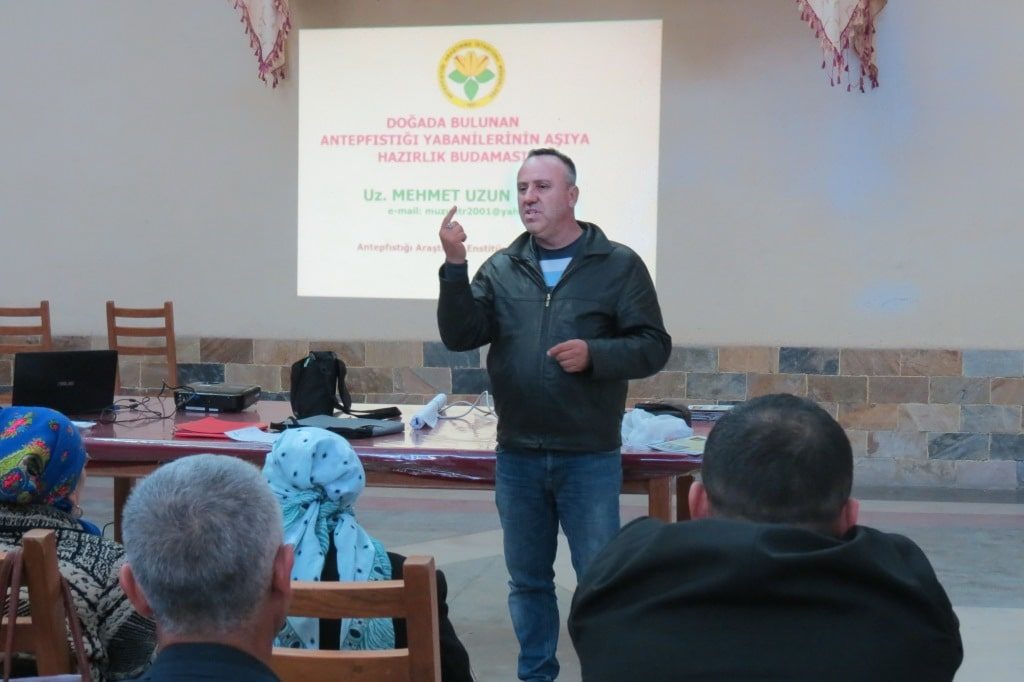
When it comes to sustainable use of land resources, important elements are the successful testing and implementation of new integrated approaches aimed at preserving and restoring ecosystems, increasing population incomes, and improving the existing resource management system. The reform processes are accompanied by knowledge and skill development, capacity building for both decision-makers and the public. The Program on a regular basis holds training seminars, workshops, field visits and study tours both within the Central Asian region and abroad.
As part of the forestry reform piloting in Kyrgyzstan, forestry sector workers participated in trainings on taxation of lands of the State Forest Fund (SFF) and legal aspects of forest and pasture use; forest management and public-private partnerships and investments in the SFF; growing seedlings and proper tree care; SFF mapping using the Quantum GIS software.
In September 2018 – May 2019, the Program held training for employees of 20 pilot leskhozes on the procedure for the formation, review and execution of leskhoz program-based budgets. The staff of five leskhozes also received training on the procedure for the formation of a stimulation fund and calculation of employee bonuses for experimental leskhozes. These training activities supported the testing and implementation of new approaches in forestry financial management, when leskhozes are empowered to distribute and use the funds. The trainings resulted in recommendations on the methodology of program-based budgeting and employee incentive system.
Educational materials, plot projects, recommendations and results of events and trainings are published on a regular basis in the form of electronic and printed materials in Kyrgyz and Russian. They are distributed to leskhozes and among the population and are easily accessible online at http://www.naturalresources-centralasia.org/index.php?id=186 and https://www.landuse-ca.org/?type=publications&year=2019&country=kyrgyzstan&lang=en.
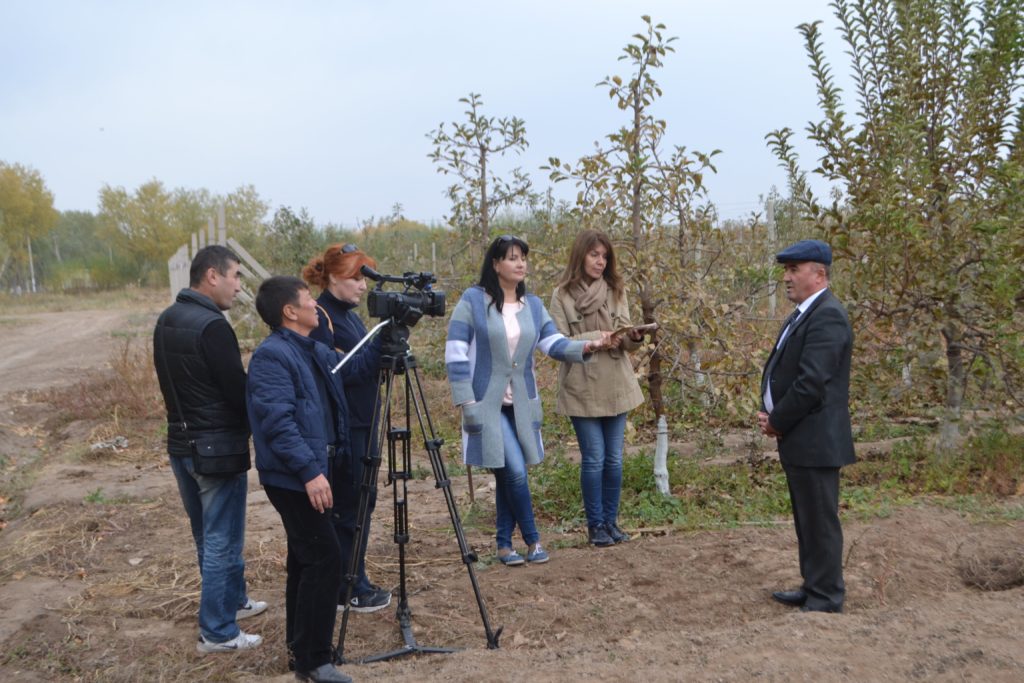
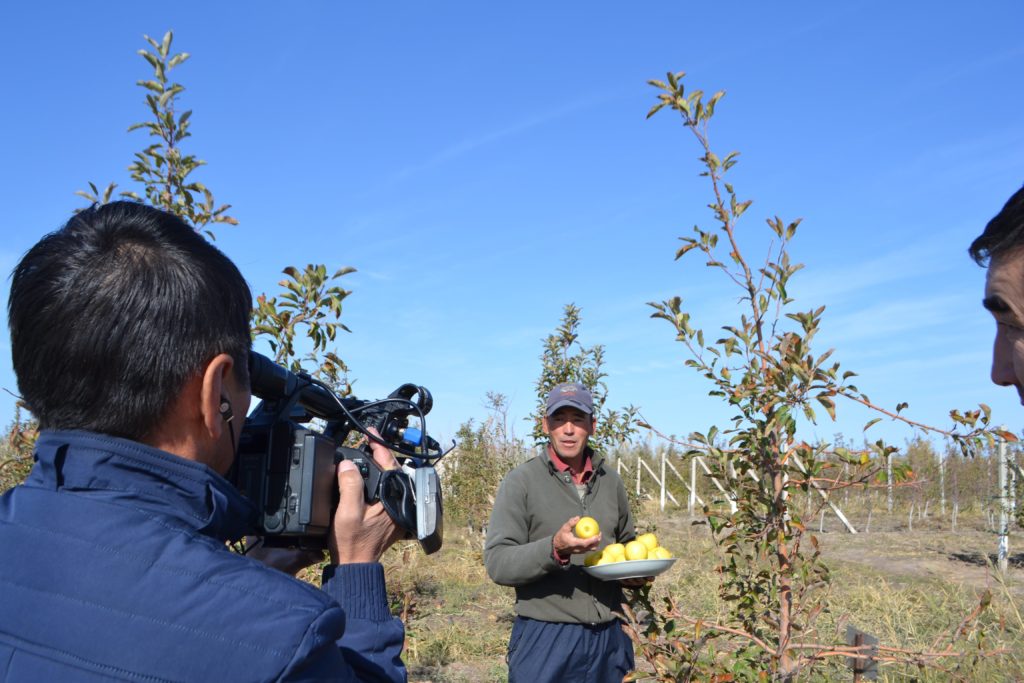
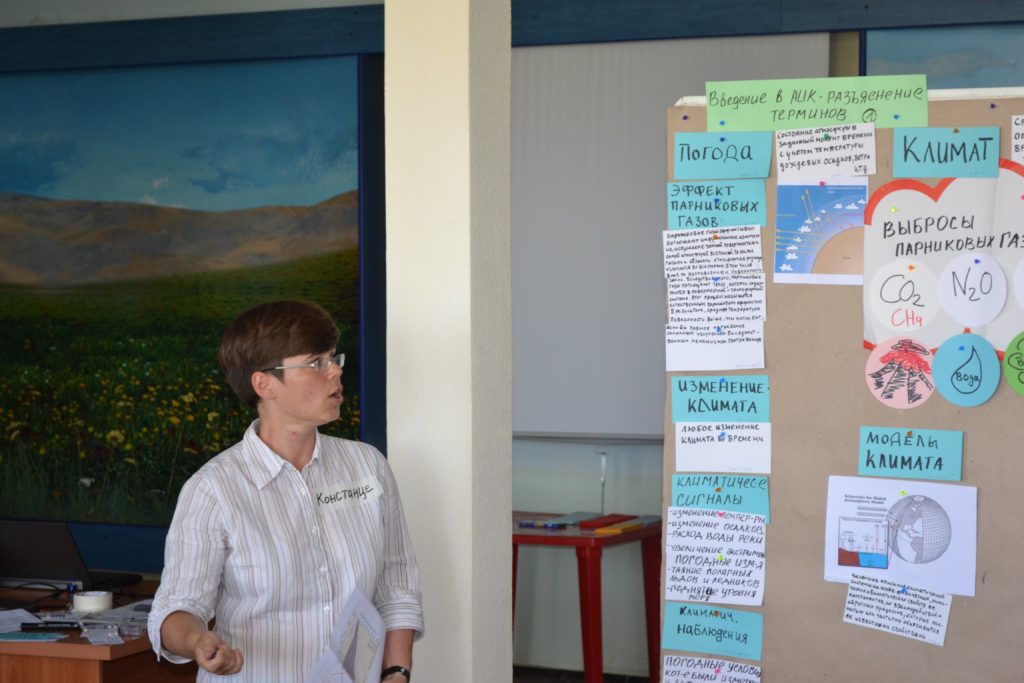
Raising awareness on sustainable land management is always crucial. In this regard, the Regional Program holds seminars, mini-lectures, press tours for representatives of the media. Specifically, journalists from Kyrgyzstan visited Georgia and produced video materials on agroforestry on various lands, the cultivation of new tree varieties in nurseries, and nature reserve management. A separate video material was dedicated to environmental education in two secondary schools that introduced modern teaching methods were introduced and classes are mostly conducted outdoors. All videos were later demonstrated by the Kyrgyz National Public Television and Radio Broadcasting Corporation.
Another joint press tour was organized in Khorezm region and Karakalpakstan in Uzbekistan, where Kyrgyz and Uzbek journalists learned about growing fruit trees on saline soils and modern agricultural technologies. The participants also visited the biosphere and tugai forests, where the project to preserve ecosystems in the Lower Amu Darya is being implemented. After the study tour, the journalists prepared materials on intensive gardening, which were demonstrated in Kyrgyzstan and published in newspapers in Uzbekistan.
In October 2017, journalists from Kyrgyzstan and Uzbekistan visited the Karakalpak branch of the Makhmum Mirzaev Research Institute of Horticulture, Viticulture and Winemaking, and the Urgench State University. In these areas, Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (German Federal Enterprise for International Cooperation) project “Sustainable Economic Development in Selected Regions of Uzbekistan”, implemented jointly with the Ministry of Agriculture and Water Resources of the Republic of Uzbekistan, supported approaches to combating land degradation through intensive landscaping on saline soils in Khorezm, Karakalpakstan and Surkhandarya.
Another successful event was a series of mini lectures on forestry sector reform, sustainable land use in the context of climate change and the necessary adaptation measures. For several days, journalists from Kyrgyzstan met with various experts and learned about measures to adapt to climate change. The materials and reports of mini lectures served as the basis for the development of a manual for the media in Russian and Kyrgyz languages.
As for environmental education and training, the Program in cooperation with the American University of Central Asia supported the development of a curriculum for students who could possible work in the field of land use in the future. In collaboration with the Kyrgyz National Television and Radio Broadcasting Corporation, the Program prepared interactive television broadcasts “Eco?Logical” that help build a sense of responsibility for the protection and preservation of natural resources in children and adolescents. The Roza Otunbayeva Foundation, together with the BIOM environmental movement, distributed these children’s programs to schools in Kyrgyzstan.
They were also included in the report of the German government at the international conference “Pursuit of Biodiversity. Germany’s international cooperation in support of the Convention on Biological Diversity for Sustainable Development” (published in October 2018)
Education (Tajikistan)
When it comes to sustainable use of land resources, important elements are the successful testing and implementation of new integrated approaches aimed at preserving and restoring ecosystems, increasing population incomes, and improving the existing resource management system. The reform processes are accompanied by knowledge and skill development, capacity building for both decision-makers and the public. The Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (German Federal Enterprise for International Cooperation) Programme regularly invites experts and organizes trainings and seminars for local partners and local residents, field visits and study tours within the Central Asian region and abroad.

In Tajikistan, the Programme supported innovations in advanced training for forestry sector employees. In particular, the Programme developed different types of manuals and training
programs that contribute to improving the quality of national education in public services, the local governance system and creating a reserve of forestry personnel. These training programs contribute to the adaptation of the education system to the requirements of the labor market in order to prepare a sufficient number of specialists who are able to carry out all forestry operations related to reforestation, care, conservation and protection. Since the integrated approach to land use in Tajikistan is based on the using the JFM approach, an appropriate training module on “Integrated Forest Management” has been developed. This module is used for training both forest users and trainers.
Exchange visits are also part of the partner and expert training. Knowledge sharing events are available here.
Education (Turkmenistan)
Since 2009, the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH Program has been supporting knowledge exchange on sustainable land management both between different sectors and at different levels, including local, national and regional.
Within the framework of activities in Turkmenistan, the Regional Program, at the request of the national partner, holds narrow technical seminars. To increase the capacity of employees of the Turkmen Hydrometeorological Service, the Program organized a climate forecasting training in September 2018 and a training on climate modeling in October 2019.
Specialists of the Land Resources Service were trained in conducting geobotanical research (October 2017) attended by experts from Mongolia and Kazakhstan.
The Program also organizes study tours on sustainable pasture management to foreign countries for Turkmen partners.
In May 2018, a government delegation involved in the development of new pasture law visited the French Pyrenees to learn about the current pasture management system.
In 2015, with the support of the program “Sustainable Development of Central Asia”, Turkmenistan developed the Law on Pastures. However, some provisions of the Law were completely new and difficult to implement in Turkmenistan. In this regard, it was necessary to develop detailed regulations. During a trip to France, Turkmen delegates could see how the French experience could be replicated in Turkmenistan. Participants noted that along with independent pastoral groups, there were groups who worked more closely with the government, which is more applicable in Turkmenistan.
The study tour participants learned that there were several pasture management systems in the French Pyrenees. Pastures are state owned but managed by users as a shared resource. Methods of organizing users, accessing pastures, and relations between users and state bodies responsible for environmental and sanitary regulation are all relevant to Turkmenistan.
For example, management decentralization to the level of users leads to increased efficiency. Most pastures are managed by livestock breeders themselves and are divided into pasture user groups (PUGs). This eliminates the need for government agencies to communicate with hundreds of individual herders. They work locally and thus have the advantage of solving local problems and planning appropriate infrastructure development. Pasture access hierarchies give preference to the needs of residents, while avoiding excessive or incomplete grazing and allowing outside users to graze on pastures based on their carrying capacity.
The delegation consisted of nine representatives of the Parliament, the Ministry of Agriculture and Water Resources, the heads of the Land Resources Service offices of Ahala and Maryi veloyats, GIZ consultants, lawyers and land use experts.
The delegation consisted of nine representatives of the Parliament, the Ministry of Agriculture and Water Resources, the heads of the Land Resources Service offices of Ahala and Maryi veloyats, GIZ consultants, lawyers and land use experts. .
Also, in March 2019, the Program specialists and experts were invited to the Scientific and Methodological Center for Sustainable Development Goals to deliver a lecture for students from various regions of Turkmenistan on the activities of the Program to achieve the SDGs. This made it possible to introduce the concept of integrated land management approaches (ILUMA) to a wide audience. The presentation was based on specific examples of sustainable pasture management as provided for by the Law of on Pastures of Turkmenistan.
Education (Uzbekistan)
When it comes to sustainable use of land resources, important elements are the successful testing and implementation of new integrated approaches aimed at preserving and restoring ecosystems, increasing population incomes, and improving the existing resource management system. The reform processes are accompanied by knowledge and skill development, capacity building for both decision-makers and the public. The Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH) Program regularly invites experts and organizes trainings and seminars for local partners and local residents, field visits and study tours within the Central Asian region and abroad.
In Uzbekistan, leskhoz employees and local residents in Kashkadarya, Samarkand and Surkhandarya regions have completed training and increased their knowledge on joint forest management. Two pilot leskhozes have tested effective land use methods on the newly created mixed plantations of sea buckthorn and wild rose, which can be an additional source of income for local residents.
Residents of the Farish district were trained in effective pasture management planning. To reduce pasture overload, people were offered opportunities to use alternative sources to generate income.
In the spring of 2018, two workshops on improving pistachio farming were held for 60 forest users in two pilot forestry enterprises – Bobotog and Gissar. An expert from the Turkish Pistachio Institute shared the Turkish experience with methods of early grafting of trees in containers. Participants learned that a high yield of pistachios is possible only after grafting, while early grafting can only be done in greenhouse containers.
In December 2018, the Program with the support of the State Forestry Committee held a seminar on the involvement of the local population in forest management at the Gissar forestry enterprise. Local residents learned how to combine pistachios and medicinal plants to increase productivity.
In May 2019, ten foresters and forest users of the Bobotog forestry enterprise improved their skills in pruning and grafting pistachio trees in a pilot area. This prepared forest users for the next grafting season.
Raising awareness on sustainable land management of both small groups and wider population is always crucial. In this regard, the Regional Program holds seminars, mini-lectures, press tours for representatives of the media.
In October 2017, journalists from Kyrgyzstan and Uzbekistan visited the Karakalpak branch of the Makhmum Mirzaev Research Institute of Horticulture, Viticulture and Winemaking, and the Urgench State University. In these areas, Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH project “Sustainable Economic Development in Selected Regions of Uzbekistan”, implemented jointly with the Ministry of Agriculture and Water Resources of the Republic of Uzbekistan, supported approaches to combating land degradation through intensive landscaping on saline soils in Khorezm, Karakalpakstan and Surkhandarya. Journalists learned about growing fruit trees on saline soils and modern agricultural technologies. After the study tour, the journalists prepared materials on intensive gardening, which were demonstrated in Kyrgyzstan and published in newspapers in Uzbekistan.

As for environmental education and training, the GIZ Program prepares TV broadcasts that help build a sense of responsibility for the protection and preservation of natural resources in children and adolescents. Similar broadcasts were successfully demonstrated by the Kyrgyz Public Television and Radio Broadcasting Corporation and distributed to schools.
All news on Uzbekistan are available here.
Management (Kazakhstan)
According to the classification of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), all Central Asian countries have little forest land. Moreover, the existing forests are mostly degraded or undergoing intensive felling. Deforestation affects the living conditions of people and wildlife and threatens the stability and equilibrium of the region’s ecosystem. Thus, the integrated protection, conservation and sustainable use of forest resources is crucial, especially in the context of climate change.
We strive to support our government and local partners in all five countries of Central Asia in amending laws and regulations, and reforming relevant government agencies and other organizations of the forestry sector. Our work is based on the principles of sustainable development aimed at environmental stability and long-term socially equitable economic benefits.
Our experts help test new management approaches at the local level, and to scale up the results at the national level. The best practical experience is available for representatives of administrative bodies and state institutions as part of regional knowledge exchange. New sustainable forest management methods that take into account local needs are developed jointly with the population and local authorities. At the national level, we assist partner ministries in adapting new methods and support the related reforms.
Through advisory support to the Committee on Forestry and Wildlife of the Ministry of Agriculture, we contribute to efforts to develop mechanisms for state support of private afforestation.
The Program experts developed recommendations on managing private forest resources based on the key elements of the government program to support private afforestation, as well as on large-scale afforestation in Kazakhstan.
The effectiveness of the government program to support afforestation is ensured by:
- a clear system for the introduction of support mechanisms, formalized as part of the sectoral afforestation strategy;
- a clear definition of the roles of all stakeholders;
- guarantee of land title.
An additional important factor is the availability of technical competencies and knowledge among private investors and technical personnel necessary for decision-making and afforestation management.
A state afforestation strategy should be adopted in order to make strategic decisions in the sector and attract private investment. The strategy should be based on reliable and relevant data on available resources, such as data on the land available for afforestation, markets and existing forest resources. Program experts will support the collection and analysis of information for a long-term vision for the development of the private forest sector and large-scale afforestation in Kazakhstan.
In addition to meeting the demand for timber, large-scale private afforestation will increase the country’s forest cover and achieve targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This can be used to attract international climate finance, which can give an initial impetus to large-scale afforestation measures.
These mechanisms are designed to stimulate investment in afforestation to create a private forest fund in the country. Six pilot plots were allocated for fast-growing tree species in Akmola, Almaty and Zhambyl regions. The technical data collected from these plots will serve as the basis for developing mechanisms f

Management (Kyrgyzstan)
According to the classification of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), all Central Asian countries have little forest land. Moreover, the existing forests are mostly degraded or undergoing intensive felling. Deforestation affects the living conditions of people and wildlife and threatens the stability and equilibrium of the region’s ecosystem. Thus, the integrated protection, conservation and sustainable use of forest resources is crucial, especially in the context of climate change.
Program experts help test new management approaches at the local level, and to scale up the results at the national level. The best practical experience is available for representatives of administrative bodies and state institutions as part of regional knowledge exchange. New sustainable forest management methods that take into account local needs are developed jointly with the population and local authorities. At the national level, we assist partner ministries in adapting new methods and support the related reforms.
We strive to support our government and local partners in all five countries of Central Asia in amending laws and regulations, and reforming relevant government agencies and other organizations of the forestry sector. Our work is based on the principles of sustainable development aimed at environmental stability and long-term socially equitable economic benefits.
In Kyrgyzstan, the State Agency on Environment Protection and Forestry (SAEPF) with our support, continues consolidating and mainstreaming new approaches to integrated forest management. These approaches imply involving the local population and local authorities in joint forest management. Testing has been conducted as part of the forestry sector reform piloting since 2015 in 20 experimental leskhozes. To coordinate piloting at the state level, a Consultative Coordinating Council has been created, which includes representatives of international and non-governmental organizations. Work is underway to amend the relevant laws and regulations.
Some of them include a Provisional Procedure for Creating an Incentive Fund and Calculating Employee Bonuses in a pilot leskhoz and the KR Government Decree No. 515 dated September 27, 2016 on the development of the draft Procedure for Use and Disposal of the State Forest Fund (SFF) and the relevant Government decree.
Based on the practical experience of piloting, a forestry sector reform concept will be developed. This experience is also used in the new SAEPF Forest Integrated Forest Ecosystem Management project, supported by the World Bank and the World Economic Forum.
Management (Tajikistan)
According to the classification of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), all Central Asian countries have little forest land. Moreover, the existing forests are mostly degraded or undergoing intensive felling. Deforestation affects the living conditions of people and wildlife and threatens the stability and equilibrium of the region’s ecosystem. Thus, the integrated protection, conservation and sustainable use of forest resources is crucial, especially in the context of climate change.
Our experts help test new management approaches at the local level, and to scale up the results at the national level. The best practical experience is available for representatives of administrative bodies and state institutions as part of regional knowledge exchange. New sustainable forest management methods that take into account local needs are developed jointly with the population and local authorities. At the national level, we assist partner ministries in adapting new methods and support the related reforms.
Forest management is a process of planning and implementing practical measures for the rational use of forests, restoring forest areas and preventing their further degradation. This process is aimed at achieving specific environmental, economic, social and sociocultural goals. Effective forestry management includes defining and concretizing goals and objectives, the successful achievement of which will ensure the sustainable management and use of forest resources, restoration and preservation of the forest’s useful functions of carbon sequestration, water flow regulation, soil erosion prevention, etc. and of water flow, prevention of soil erosion, etc., as well as their economic and social functions.
A forest management plan includes a implies of a plan of forestry activities (e.g. forest inventory, yield calculation, harvesting of wood and non-timber forest products, silvicultural activities, protection and monitoring) that indicates goals, objectives and control mechanisms in the forest area. Also, a forest management plan is an important tool to ensure the participation and awareness of people living in or near forests and other stakeholders.
Tajikistan uses a landscape approach to forest management that takes into account climate change. Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH introduced the Joint Forest Management (JFM) approach, which helps local residents and leskhozes to jointly manage forest areas, restore degraded areas, and resolve conflicts between forest and pasture users. The JFM approach is based on long-term contracts between forest users and leskhozes. Local residents get the right to use the forest area, and in return undertake to restore the degraded territories. In addition to that, the local population, together with the leskhoz, is involved in the planning and management of forests, and in monitoring activities and results.
Comprehensive land management measures are incorporated in management plans and annual plans to ensure sustainable forest management. Women are also involved in forest management processes.
The GIZ Program also supported the modernization of TajFIS – Tajikistan Forest Management Information System, a comprehensive system used to support the planning, implementation and monitoring of forest management activities. It also allows keeping current forest cadasters and mapping spatial data. This means that the characteristics of the subjects such as the population of the village and their location, can be depicted on the map. The components of TajFIS, which will necessarily be interconnected, include the Information Monitoring System (IMS), Geographic Information System (GIS) and KDMS (K-link).[/vc_column_text][vc_empty_space][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”2/3″][vc_column_text]Through GIZ expert support, new standards have been developed for modeling business processes and network services on the basis of the existing forestry work processes and in accordance with the BPMN (Business Process Modeling Notation) standards. This system allows creating workflow diagrams that can later be visualized, analyzed and reproduced by other stakeholders. Currently, this system is being piloted in two forestry enterprises in Gorno-Badakhshan region.
Pasture User Unions (PUUs) have been established at the jamoat (rural municipality) level and includes representatives from several villages. This is an official organization that has articles, a legal registration, a seal and a bank account. Within PUUs, members can work together to solve current problems and plan future collaborations such as control of livestock grazing, monitoring of pasture conditions, rehabilitation of pasture corridors, monitoring of animal health, organizing livestock vaccination and, most importantly, protecting the interests of each PUU member to ensure safe access to pastures.
Excessive grazing, especially in pastures near villages, worsens the condition of the land. Land degradation reduces pasture productivity and poses a threat to food security and livelihoods of the rural population in Tajikistan. Despite the adoption of the Law on Pastures in 2013, the mechanisms of livestock grazing control are not yet widely practiced by local communities. The main reasons are the lack of relevant regulations and weak law enforcement. Consequently, sustainable pasture management planning is an essential tool to be used by pasture users.
Management (Turkmenistan)
According to the classification of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), all Central Asian countries have little forest land. Moreover, the existing forests are mostly degraded or undergoing intensive felling. Deforestation affects the living conditions of people and wildlife and threatens the stability and equilibrium of the region’s ecosystem. Thus, the integrated protection, conservation and sustainable use of forest resources is crucial, especially in the context of climate change.
We strive to support our government and local partners in all five countries of Central Asia in amending laws and regulations, and reforming relevant government agencies and other organizations of the forestry sector. Our work is based on the principles of sustainable development aimed at environmental stability and long-term socially equitable economic benefits.
To promote sustainable land use in Turkmenistan, the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH has been successfully collaborating with the Ministry of Agriculture and Environment Protection and its departments. One of the main areas at the national level is assistance in promoting sustainable pasture management and improving pasture and forest legislation. Specifically, GIZ has contributed to the development of the Law on Pastures and the Forest Code. Also, together with international and national experts, GIZ Program was involved in developing of relevant regulations which are currently under approval by the Ministry of Agriculture and Environment Protection.
Management (Uzbekistan)
According to the classification of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), all Central Asian countries have little forest land. Moreover, the existing forests are mostly degraded or undergoing intensive felling. Deforestation affects the living conditions of people and wildlife and threatens the stability and equilibrium of the region’s ecosystem. Thus, the integrated protection, conservation and sustainable use of forest resources is crucial, especially in the context of climate change.
Program experts help test new management approaches at the local level, and to scale up the results at the national level. The best practical experience is available for representatives of administrative bodies and state institutions as part of regional knowledge exchange. New sustainable forest management methods that take into account local needs are developed jointly with the population and local authorities. At the national level, we assist partner ministries in adapting new methods and support the related reforms.
The Regional Program of Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH strives to support government and local partners in all five countries of Central Asia in amending laws and regulations, and reforming relevant government agencies and other organizations of the forestry sector. Our work is based on the principles of sustainable development aimed at environmental stability and long-term socially equitable economic benefits.
In Uzbekistan, joint forest management approaches are piloted on three demonstration plots of Bobotog forestry enterprise, Surkhandarya region, planted with pistachio trees. Read more about piloting here.
Through GIZ support, leskhoz employees and local residents in Kashkadarya, Samarkand and Surkhandarya regions have increased their knowledge on joint forest management. Two pilot leskhozes have tested effective land management methods on the newly created mixed plantations of sea buckthorn and wild rose, which can be an additional source of income for local residents.
Knowledge Exchange (Central Asia)
Since 2009, the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH Program has been supporting knowledge exchange on sustainable land management both between different sectors and at different levels, including local, national and regional.
One of the important steps was the creation of the Regional Environmental Expert Network of Central Asia (GREEN Central Asia), which brings together organizations and independent experts from various sectors. GREEN CA aims to strengthen communication between specialists and their involvement in the development of various development projects and strategic planning processes in the Central Asian region. Their expertise helps implementing sustainable use of natural resources and the ideas of a green economy and low carbon development. The main element of the network is a consortium between Karaganda Ecological Museum and the NGO CAMP Alatoo (Kyrgyzstan).
In 2017, the Central Asian Regional Pasture Network became part of GREEN CA, created to facilitate the exchange of experience and knowledge in the field of pasture management in the region, China and Mongolia. The work of the Network contributes to the dissemination of successful models and approaches in all countries, as it includes both individual practitioners and representatives of organizations and projects. Specifically, in August 2014, the Program supported a study tour to Kyrgyzstan for representatives of government agencies and non-governmental organizations from Tajikistan and Turkmenistan. During the study tour, participants learned about the pasture management experience of Kyrgyzstan and developed joint recommendations for improvement in all three countries.
In 2014, Bishkek hosted the Practitioners’ Conference on Advancement of Sustainable Pasture Management in Central Asia. The purpose of this event for politicians and practitioners from Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan and international experts was to exchange experience and knowledge and join efforts to promote reforms in the pasture sector. Representatives of Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan had the opportunity to learn about international experience and the experience of their Kyrgyz and Tajik colleagues.
Conference participants were provided with innovative tools and approaches to managing grazing lands, as well as proven mechanisms and processes. The program of the event included a field visit to one of the pasture committees in Chui oblast.
Some of the Important outcomes of the conference were the exchange of experience and knowledge, discussion of further actions and documentation of best practices and approaches. In addition to that, the results of the conference, an overview of the situation in the countries of the Central Asian region, analysis, comments and recommendations were included in the brochure “Sustainable Pasture Management in Central Asia”.
Field visits in Central Asia and study tours abroad help the exchange of experience and continuous training of practitioners and decision makers. Specifically, over the course of several years, long-term and short-term exchange visits were organized between representatives of the forestry services of Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan.
Besides, the Program conducted regional events such as:
- Regional expert seminar “Regional Strategic Approach to Adaptation to Climate Change in the Mountainous Regions of Central Asia” (Almaty, Kazakhstan, 19-21 December 2016)
- International conference “Economics of Land Degradation in Central Asia” (Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan, 28-29 November 2016)
- International round table “Sustainable Use and Conservation of Wild Animals in Tajikistan” (Dushanbe, Tajikistan, 2-3 November 2016)
- International Conference on Natural Capital for the Transition to a Green Economy (Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan, 30 June – 1 July 2016)
- International Conference on Sustainable Wildlife Management in Central Asia: Practical Experience and Next Steps (September 1-3, 2015 Ashgabat, Turkmenistan)
- International Conference “Ecosystem-Based Approach to Adaptation to Climate Change in Central Asia” (Dushanbe, Tajikistan, 9 April 2015)
These events help specialists to learn about the features and advantages of various natural resource management systems and establish long-term cooperation.
Knowledge Exchange (Kazakhstan)
Since 2009, the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH Program has been supporting knowledge exchange on sustainable land management both between different sectors and at different levels, including local, national and regional.
One of the important steps was the creation of the Regional Environmental Expert Network of Central Asia (GREEN Central Asia), which brings together organizations and independent experts from various sectors. GREEN CA aims to strengthen communication between specialists and their involvement in the development of various development projects and strategic planning processes in the Central Asian region. Their expertise helps implementing sustainable use of natural resources and the ideas of a green economy and low carbon development. The main element of the network is a consortium between Karaganda Ecological Museum and the NGO CAMP Alatoo (Kyrgyzstan).
In 2017, the Central Asian Regional Pasture Network became part of GREEN CA, created to facilitate the exchange of experience and knowledge in the field of pasture management in the region, China and Mongolia. The work of the Network contributes to the dissemination of successful models and approaches in all countries, as it includes both individual practitioners and representatives of organizations and projects.
Specifically, in August 2014, the Program supported a study tour to Kyrgyzstan for representatives of government agencies and non-governmental organizations from Tajikistan and Turkmenistan. During the study tour, participants learned about the pasture management experience of Kyrgyzstan and developed joint recommendations for improvement in all three countries.
In 2014, Bishkek hosted the Practitioners’ Conference on Advancement of Sustainable Pasture Management in Central Asia. The purpose of this event for politicians and practitioners from Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan and international experts was to exchange experience and knowledge and join efforts to promote reforms in the pasture sector. Representatives of Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan had the opportunity to learn about international experience and the experience of their Kyrgyz and Tajik colleagues.
Conference participants were provided with innovative tools and approaches to managing grazing lands, as well as proven mechanisms and processes. The program of the event included a field visit to one of the pasture committees in Chui oblast. Some of the Important outcomes of the conference were the exchange of experience and knowledge, discussion of further actions and documentation of best practices and approaches.
In addition to that, the results of the conference, an overview of the situation in the countries of the Central Asian region, analysis, comments and recommendations were included in the brochure “Sustainable Pasture Management in Central Asia”.
SIC ICSD employees actively participate and contribute to the events organized by the Program in Turkmenistan. In particular, the head of the ICSD Secretariat Mr. Batyr Mammadov made a presentation during the seminar for journalists “Climate Change and Pastures in Turkmenistan” (Ashgabat, February 2019) on the impact of climate change on desert pasture productivity, and his colleague Mr. Kurban Allaberdiev shared with journalists the climate policy pursued by the country and told about the progress in revising the National Climate Change Strategy of Turkmenistan.
As a contact person from Turkmenistan for the UNFCCC, Mr. Allaberdiev also participated in seminars on climate change and climate forecasts (September 2018) for the Hydrometeorological Service and experts involved in the preparation of National Communications to the UNFCCC.
Field visits in Central Asia and study tours abroad help the exchange of experience and continuous training of practitioners and decision makers.
Specifically, a training seminar for journalists “Climate Change and Pastures in Turkmenistan” was an excellent opportunity for GIZ colleagues from Kyrgyzstan and partners to more deeply explain the current issues and challenges related to climate change (Ashgabat, 2019). Turkmen experts from SIC ICSD and the UNFCCC Focal Point shared with journalists the climate policy pursued by Turkmenistan and the main points of the National Climate Change Strategy. Also, experts spoke about the impact that climate change on the productivity of pastures, a very important natural resource that Turkmenistan is rich in. An interesting and constructive dialogue between the expert community and journalists of the two countries, as well as the exchange of experience and knowledge between the media workers of the national print media and television channels and their colleagues from all five regions was highly appreciated by the Turkmen side and extensively covered in the mass media.
Another tool to facilitate the exchange of experience is the development of an ICSD information policy and document management system. The ICSD decision approved the introduction of a modern and convenient online tool – K-Link. In order to pilot the tool, the SIC head office in Ashgabat and its branch in Kazakhstan were provided with a k-box that allows storing files in electronic form and regulating access to the organization’s database. The Regional Program held introductory workshops for SIC ICSD employees in Ashgabat (2018) on the tool. Later that year, SIC ICSD in Ashgabat and its branch in Kazakhstan decided to open to each other access to the organization’s internal documents through mutual authorization of access to the k-box of each country.
Another example is a technical seminar on enhancing the forecasting capacity of employees of the Turkmen Hydrometeorological Service (September 2018). The event was held by a
Program expert and employees of the Kyrgyz Hydrometeorological Service. The exchange of experience and knowledge between hydrometeorological services of the two countries lasted for two days.
In May 2018, a government delegation involved in the development of new pasture law visited the French Pyrenees to learn about the current pasture management system.
In 2015, with the support of the program “Sustainable Development of Central Asia”, Turkmenistan developed the Law on Pastures. However, some provisions of the Law were completely new and difficult to implement in Turkmenistan. In this regard, it was necessary to develop detailed regulations. During a trip to France, Turkmen delegates could see how the French experience could be replicated in Turkmenistan. Participants noted that along with independent pastoral groups, there were groups who worked more closely with the government, which is more applicable in Turkmenistan.
The study tour participants learned that there were several pasture management systems in the French Pyrenees. Pastures are state owned but managed by users as a shared resource. Methods of organizing users, accessing pastures, and relations between users and state bodies responsible for environmental and sanitary regulation are all relevant to Turkmenistan.
For example, management decentralization to the level of users leads to increased efficiency. Most pastures are managed by livestock breeders themselves and are divided into pasture user groups (PUGs). This eliminates the need for government agencies to communicate with hundreds of individual herders. They work locally and thus have the advantage of solving local problems and planning appropriate infrastructure development. Pasture access hierarchies give preference to the needs of residents, while avoiding excessive or incomplete grazing and allowing outside users to graze on pastures based on their carrying capacity.
The delegation consisted of nine representatives of the Parliament, the Ministry of Agriculture and Water Resources, the heads of the Land Resources Service offices of Ahala and Maryi veloyats, GIZ consultants, lawyers and land use experts.
Knowledge Exchange(Kyrgyzstan)
Since 2009, the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH Program has been supporting knowledge exchange on sustainable land management both between different sectors and at different levels, including local, national and regional.
One of the important steps was the creation of the Regional Environmental Expert Network of Central Asia (GREEN Central Asia), which brings together organizations and independent experts from various sectors. GREEN CA aims to strengthen communication between specialists and their involvement in the development of various development projects and strategic planning processes in the Central Asian region. Their expertise helps implementing sustainable use of natural resources and the ideas of a green economy and low carbon development. The main element of the network is a consortium between Karaganda Ecological Museum and the NGO CAMP Alatoo (Kyrgyzstan).
In 2017, the Central Asian Regional Pasture Network became part of GREEN CA, created to facilitate the exchange of experience and knowledge in the field of pasture management in the region, China and Mongolia. The work of the Network contributes to the dissemination of successful models and approaches in all countries, as it includes both individual practitioners and representatives of organizations and projects. Specifically, in August 2014, the Program supported a study tour to Kyrgyzstan for representatives of government agencies and non-governmental organizations from Tajikistan and Turkmenistan. During the study tour, participants learned about the pasture management experience of Kyrgyzstan and developed joint recommendations for improvement in all three countries.
In 2014, Bishkek hosted the Practitioners’ Conference on Advancement of Sustainable Pasture Management in Central Asia. The purpose of this event for politicians and practitioners from Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan and international experts was to exchange experience and knowledge and join efforts to promote reforms in the pasture sector. Representatives of Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan had the opportunity to learn about international experience and the experience of their Kyrgyz and Tajik colleagues.
Conference participants were provided with innovative tools and approaches to managing grazing lands, as well as proven mechanisms and processes. The program of the event included a field visit to one of the pasture committees in Chui oblast.
Some of the Important outcomes of the conference were the exchange of experience and knowledge, discussion of further actions and documentation of best practices and approaches. In addition to that, the results of the conference, an overview of the situation in the countries of the Central Asian region, analysis, comments and recommendations were included in the brochure “Sustainable Pasture Management in Central Asia”.
Field visits in Central Asia and study tours abroad help the exchange of experience and continuous training of practitioners and decision makers. Specifically, over the course of several years, long-term and short-term exchange visits were organized between representatives of the forestry services of Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. Specialists learned about the features and advantages of various natural resource management systems and established long-term cooperation.
At the national level, a Coordinating Consultative Council (CCC) also contributes to the dissemination of practical experience of projects implemented in the forestry sector with the support of various development partners. The results of CCC meetings are published in the quarterly newsletter.
Knowledge Exchange (Tajikistan)
ince 2009, the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH Program has been supporting knowledge exchange on sustainable land management both between different sectors and at different levels, including local, national and regional.
One of the important steps was the creation of the Regional Environmental Expert Network of Central Asia (GREEN Central Asia), which brings together organizations and independent experts from various sectors. GREEN CA aims to strengthen communication between specialists and their involvement in the development of various development projects and strategic planning processes in the Central Asian region. Their expertise helps implementing sustainable use of natural resources and the ideas of a green economy and low carbon development. The main element of the network is a consortium between Karaganda Ecological Museum and the NGO CAMP Alatoo (Kyrgyzstan).
In 2017, the Central Asian Regional Pasture Network became part of GREEN CA, created to facilitate the exchange of experience and knowledge in the field of pasture management in the region, China and Mongolia. The work of the Network contributes to the dissemination of successful models and approaches in all countries, as it includes both individual practitioners and representatives of organizations and projects.
Specifically, in August 2014, the Program supported a study tour to Kyrgyzstan for representatives of government agencies and non-governmental organizations from Tajikistan and Turkmenistan. During the study tour, participants learned about the pasture management experience of Kyrgyzstan and developed joint recommendations for improvement in all three countries.
In 2014, Bishkek hosted the Practitioners’ Conference on Advancement of Sustainable Pasture Management in Central Asia. The purpose of this event for politicians and practitioners from Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan and international experts was to exchange experience and knowledge and join efforts to promote reforms in the pasture sector. Representatives of Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan had the opportunity to learn about international experience and the experience of their Kyrgyz and Tajik colleagues.
Conference participants were provided with innovative tools and approaches to managing grazing lands, as well as proven mechanisms and processes. The program of the event included a field visit to one of the pasture committees in Chui oblast.
Some of the Important outcomes of the conference were the exchange of experience and knowledge, discussion of further actions and documentation of best practices and approaches. In addition to that, the results of the conference, an overview of the situation in the countries of the Central Asian region, analysis, comments and recommendations were included in the brochure “Sustainable Pasture Management in Central Asia”.
Field visits in Central Asia and study tours abroad help the exchange of experience and continuous training of practitioners and decision makers. Specifically, over the course of several years, long-term and short-term exchange visits were organized between representatives of the forestry services of Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. Specialists learned about the features and advantages of various natural resource management systems and established long-term cooperation.
Knowledge Exchange (Turkmenistan)
Since 2009, the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH Program has been supporting knowledge exchange on sustainable land management both between different sectors and at different levels, including local, national and regional.
One of the important steps was the creation of the Regional Environmental Expert Network of Central Asia (GREEN Central Asia), which brings together organizations and independent experts from various sectors. GREEN CA aims to strengthen communication between specialists and their involvement in the development of various development projects and strategic planning processes in the Central Asian region. Their expertise helps implementing sustainable use of natural resources and the ideas of a green economy and low carbon development. The main element of the network is a consortium between Karaganda Ecological Museum and the NGO CAMP Alatoo (Kyrgyzstan).
In 2017, the Central Asian Regional Pasture Network became part of GREEN CA, created to facilitate the exchange of experience and knowledge in the field of pasture management in the region, China and Mongolia. The work of the Network contributes to the dissemination of successful models and approaches in all countries, as it includes both individual practitioners and representatives of organizations and projects.
Specifically, in August 2014, the Program supported a study tour to Kyrgyzstan for representatives of government agencies and non-governmental organizations from Tajikistan and Turkmenistan. During the study tour, participants learned about the pasture management experience of Kyrgyzstan and developed joint recommendations for improvement in all three countries.
In 2014, Bishkek hosted the Practitioners’ Conference on Advancement of Sustainable Pasture Management in Central Asia. The purpose of this event for politicians and practitioners from Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan and international experts was to exchange experience and knowledge and join efforts to promote reforms in the pasture sector. Representatives of Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan had the opportunity to learn about international experience and the experience of their Kyrgyz and Tajik colleagues.
Conference participants were provided with innovative tools and approaches to managing grazing lands, as well as proven mechanisms and processes.
The program of the event included a field visit to one of the pasture committees in Chui oblast. Some of the Important outcomes of the conference were the exchange of experience and knowledge, discussion of further actions and documentation of best practices and approaches. In addition to that, the results of the conference, an overview of the situation in the countries of the Central Asian region, analysis, comments and recommendations were included in the brochure “Sustainable Pasture Management in Central Asia”.
SIC ICSD employees actively participate and contribute to the events organized by the Program in Turkmenistan. In particular, the head of the ICSD Secretariat Mr. Batyr Mammadov made a presentation during the seminar for journalists “Climate Change and Pastures in Turkmenistan” (Ashgabat, February 2019) on the impact of climate change on desert pasture productivity, and his colleague Mr. Kurban Allaberdiev shared with journalists the climate policy pursued by the country and told about the progress in revising the National Climate Change Strategy of Turkmenistan.
As a contact person from Turkmenistan for the UNFCCC, Mr. Allaberdiev also participated in seminars on climate change and climate forecasts (September 2018) for the Hydrometeorological Service and experts involved in the preparation of National Communications to the UNFCCC.
Field visits in Central Asia and study tours abroad help the exchange of experience and continuous training of practitioners and decision makers.
Specifically, a training seminar for journalists “Climate Change and Pastures in Turkmenistan” was an excellent opportunity for GIZ colleagues from Kyrgyzstan and partners to more deeply explain the current issues and challenges related to climate change (Ashgabat, 2019). Turkmen experts from SIC ICSD and the UNFCCC Focal Point shared with journalists the climate policy pursued by Turkmenistan and the main points of the National Climate Change Strategy. Also, experts spoke about the impact that climate change on the productivity of pastures, a very important natural resource that Turkmenistan is rich in. An interesting and constructive dialogue between the expert community and journalists of the two countries, as well as the exchange of experience and knowledge between the media workers of the national print media and television channels and their colleagues from all five regions was highly appreciated by the Turkmen side and extensively covered in the mass media.
Another tool to facilitate the exchange of experience is the development of an ICSD information policy and document management system. The ICSD decision approved the introduction of a modern and convenient online tool – K-Link. In order to pilot the tool, the SIC head office in Ashgabat and its branch in Kazakhstan were provided with a k-box that allows storing files in electronic form and regulating access to the organization’s database. The Regional Program held introductory workshops for SIC ICSD employees in Ashgabat (2018) on the tool. Later that year, SIC ICSD in Ashgabat and its branch in Kazakhstan decided to open to each other access to the organization’s internal documents through mutual authorization of access to the k-box of each country.
Another example is a technical seminar on enhancing the forecasting capacity of employees of the Turkmen Hydrometeorological Service (September 2018). The event was held by a
Program expert and employees of the Kyrgyz Hydrometeorological Service. The exchange of experience and knowledge between hydrometeorological services of the two countries lasted for two days.
In May 2018, a government delegation involved in the development of new pasture law visited the French Pyrenees to learn about the current pasture management system.
In 2015, with the support of the program “Sustainable Development of Central Asia”, Turkmenistan developed the Law on Pastures. However, some provisions of the Law were completely new and difficult to implement in Turkmenistan. In this regard, it was necessary to develop detailed regulations. During a trip to France, Turkmen delegates could see how the French experience could be replicated in Turkmenistan. Participants noted that along
with independent pastoral groups, there were groups who worked more closely with the government, which is more applicable in Turkmenistan.
The study tour participants learned that there were several pasture management systems in the French Pyrenees. Pastures are state owned but managed by users as a shared resource. Methods of organizing users, accessing pastures, and relations between users and state bodies responsible for environmental and sanitary regulation are all relevant to Turkmenistan.
For example, management decentralization to the level of users leads to increased efficiency. Most pastures are managed by livestock breeders themselves and are divided into pasture user groups (PUGs). This eliminates the need for government agencies to communicate with hundreds of individual herders. They work locally and thus have the advantage of solving local problems and planning appropriate infrastructure development. Pasture access hierarchies give preference to the needs of residents, while avoiding excessive or incomplete grazing and allowing outside users to graze on pastures based on their carrying capacity.
The delegation consisted of nine representatives of the Parliament, the Ministry of Agriculture and Water Resources, the heads of the Land Resources Service offices of Ahala and Maryi veloyats, GIZ consultants, lawyers and land use experts.
Knowledge Exchange (Uzbekistan)
Since 2009, the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH Program has been supporting knowledge exchange on sustainable land management both between different sectors and at different levels, including local, national and regional.
One of the important steps was the creation of the Regional Environmental Expert Network of Central Asia (GREEN Central Asia), which brings together organizations and independent experts from various sectors. GREEN CA aims to strengthen communication between specialists and their involvement in the development of various development projects and strategic planning processes in the Central Asian region. Their expertise helps implementing sustainable use of natural resources and the ideas of a green economy and low carbon development. The main element of the network is a consortium between Karaganda Ecological Museum and the NGO CAMP Alatoo (Kyrgyzstan).
In 2017, the Central Asian Regional Pasture Network became part of GREEN CA, created to facilitate the exchange of experience and knowledge in the field of pasture management in the region, China and Mongolia. The work of the Network contributes to the dissemination of successful models and approaches in all countries, as it includes both individual practitioners and representatives of organizations and projects. Specifically, in August 2014, the Program supported a study tour to Kyrgyzstan for representatives of government agencies and non-governmental organizations from Tajikistan and Turkmenistan. During the study tour, participants learned about the pasture management experience of Kyrgyzstan and developed joint recommendations for improvement in all three countries.
In 2014, Bishkek hosted the Practitioners’ Conference on Advancement of Sustainable Pasture Management in Central Asia. The purpose of this event for politicians and practitioners from Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan and international experts was to exchange experience and knowledge and join efforts to promote reforms in the pasture sector. Representatives of Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan had the opportunity to learn about international experience and the experience of their Kyrgyz and Tajik colleagues.
Conference participants were provided with innovative tools and approaches to managing grazing lands, as well as proven mechanisms and processes. The program of the event included a field visit to one of the pasture committees in Chui oblast.
Some of the Important outcomes of the conference were the exchange of experience and knowledge, discussion of further actions and documentation of best practices and approaches. In addition to that, the results of the conference, an overview of the situation in the countries of the Central Asian region, analysis, comments and recommendations were included in the brochure “Sustainable Pasture Management in Central Asia”.
Field visits in Central Asia and study tours abroad help the exchange of experience and continuous training of practitioners and decision makers. In particular, at the end of January 2017, the Program organized a visit of the State Complex delegation to the Republic of Turkey was to study the experience of pistachio growing. This resulted in a memorandum of understanding between the forest departments of the Republic of Uzbekistan and Turkey. Also, a specialist in pistachio growing from the Turkish Institute of Pistachio Growing was invited to conduct a training workshop on methods for caring for pistachio forests in the Surkhandarya region.
In 2017, together with the program of the Korea International Cooperation Agency (KOICA), the Program organized a study tour of the Uzbek delegation to the Republic of Korea on the cultivation, collection and processing of medicinal. Representatives of various Uzbek departments, ministries, and farming associations also traveled to Bishkek to learn about pasture management practices. The study tour was organized by the Program with the support of the UNDP land management project.